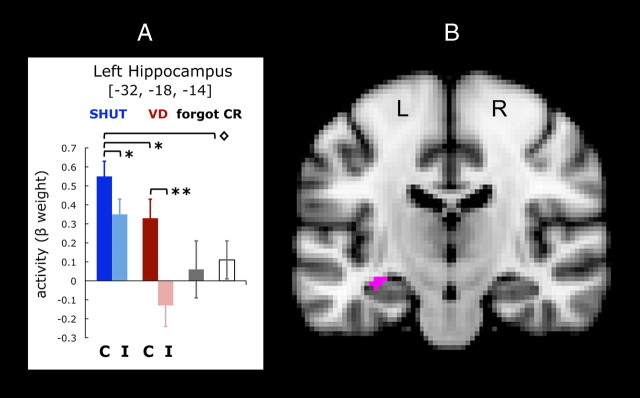
Figure 3.
Univariate results. Activity in the left hippocampus increased selectively in association with recollection. The ANOVA of whole-brain activity that compared factors for SHUT correct, SHUT incorrect, VD correct, VD incorrect, forgot and correct rejections (CR) identified this functional region of interest (voxelwise threshold, p < 0.001; p corrected <0.05) that evidenced an interaction of memory performance and conditions. A, Mean values were extracted for the β-activity associated with each of the six categories of responses, and the analysis revealed that activity associated with recollection was negatively impacted by interference from visual distraction, such that VD correct was diminished relative to SHUT correct. On the x-axis, C indicates recognition when recall was correct, and I indicates recognition with incorrect recall. Error bars represent the SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001; ◇ indicates the differences for SHUT correct between forgot and CR, p < 0.05. B, The left hippocampus cluster (25 voxels) is shown on a coronal view of the MNI brain template.