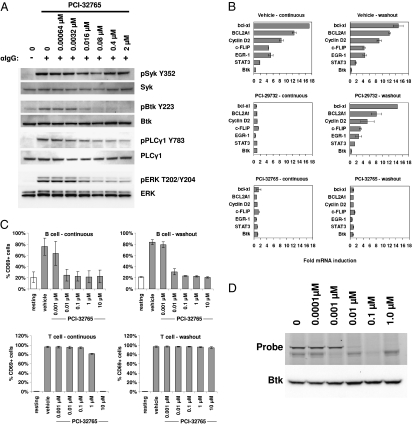
Fig. 3.
Inhibition of B-cell receptor signaling. (A) Concentration-dependent inhibition of BCR stimulation-induced phosphorylation events in DOHH2 cells. Cells were exposed to PCI-32765 and then drug was washed out before stimulation with anti-IgG. Blots were probed with the indicated antibodies. (B) Comparison of the reversible Btk inhibitor PCI-29732 to the irreversible Btk inhibitor PCI-32765 on the transcriptional response of six genes induced by BCR stimulation. Purified human peripheral B cells were treated with vehicle or 1 μM inhibitor for 1 h and then stimulated for 6 h with anti-IgM. In the washout condition, inhibitor-containing cell media was replaced with fresh media before addition of anti-IgM. Gene expression levels (mean ± SD) were measured by TaqMan RT-PCR and normalized to unstimulated cells. Btk expression is not affected by BCR stimulation or drug treatment. (C) Concentration-dependent inhibition of antigen receptor stimulation induced cell surface expression of the lymphocyte activation marker CD69 (mean ± SD). Purified human B or T cells were treated with PCI-32765 for 1 h and then stimulated for 18 h. In the washout condition, inhibitor-containing cell media was replaced with fresh media before stimulation. (D) Concentration-dependent covalent binding of PCI-32765 to Btk in purified human B cells as measured by the ability of Btk to bind to the fluorescent affinity probe PCI-33380. Total Btk levels are measured by Western blot (Bottom).