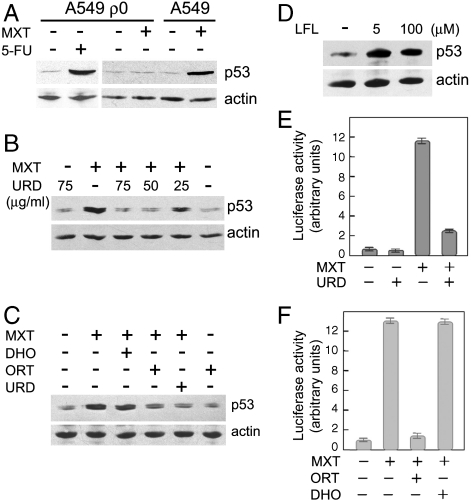
Fig. 3.
DHODH deficiency leads to up-regulation of p53 in response to myxothiazol. (A) Myxothiazol fails to activate p53 in the ρ0 cells. Western analysis of p53 levels in A549 ρ0 and A549 wt cells exposed to 2 μM myxothiazol (MXT) or 5-FU (10 μg/ml) for 18 h. (B and C) Uridine and orotate (but not dihydroorotate) suppress myxothiazol-induced accumulation of p53. Western analysis of p53 in RKO cells exposed to 1 μM myxothiazol (MXT) for 16 h in the presence of indicated concentrations of uridine (URD) (B) or in the presence of 50 μg/ml uridine (URD) or 1 mM orotate (ORT) or 1 mM dihydroorotate (DHO) (C). (D) Western analysis of p53 in HeLa cells exposed to 5 or 100 μM DHODH inhibitor leflunomide (LFL) for 48 h. (E and F) Uridine and orotate (but not dihydroorotate) suppress myxothiazol-induced activation of the p53-dependent reporter. Luciferase reporter assay of p53-dependent transcription in HeLa cells exposed to 1 μM myxothiazol (MXT) for 22 h in the presence of 50 μg/ml uridine (URD) (E) or in the presence of 1 mM orotate (ORT) or 1 mM dihydroorotate (DHO) (F).