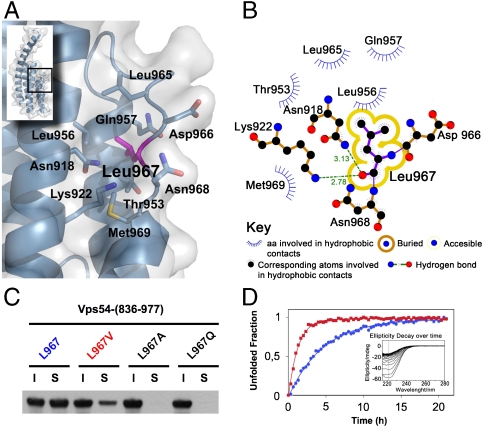
Fig. 2.
Leu967 interactions contribute to D-domain stability. (A) Stick model shown under translucent surface of the main hydrophobic pocket in the vicinity of L967 highlighted in magenta. (B) Diagram showing hydrophobic contacts, hydrogen bonds and solvent accessibility of L967. (C) Soluble (S) and insoluble (I) fractions of wild-type and mutant (L967V, L967A, and wobbler) GST-Vps54-CT after overexpression in E. coli. Proteins were detected by immunoblotting with antibody to GST conjugated to HRP. (D) Unfolding rate of wild-type (blue circles) and L967V mutant (red squares) Vps54-CT measured by ellipticity decay at 222 nm over time at 30 °C (inset shows raw data for the L967V mutant). Normalized ellipticity signal was used to calculate the decay rate constant from nonlinear-curve fitting.