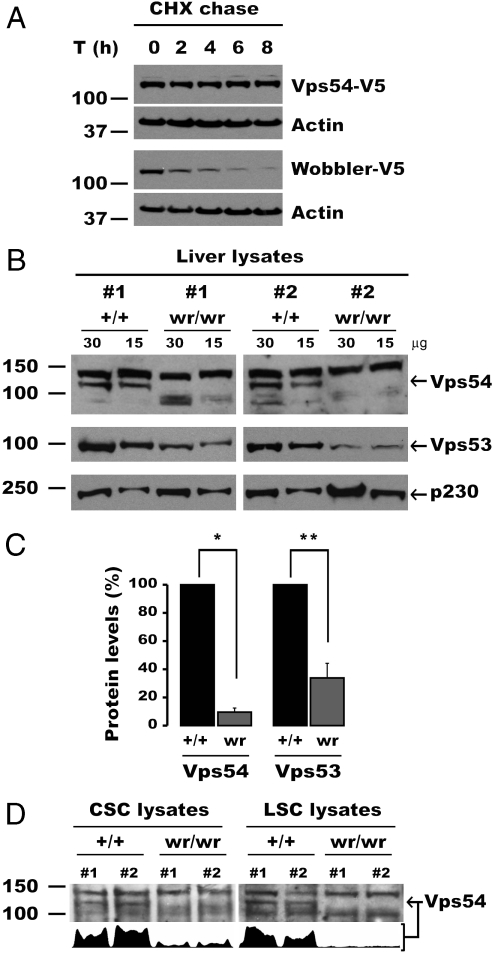
Fig. 4.
The L967Q mutation destabilizes Vps54, resulting in reduced levels of GARP in the wobbler mouse. (A) Stability of Vps54 alleles analyzed by cycloheximide (CHX) chase. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with the indicated Vps54 constructs for 16 h, after which CHX was added to the medium to stop protein synthesis, and aliquots of cells were taken at different time points. Ten micrograms of lysate protein per lane were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibody to the V5 tag. A nonspecific reactive band of around 57 kDa was used as an internal loading control. One representative experiment out of three with similar results is shown. (B–D) Reduced levels of Vps54 and GARP in the wobbler mouse. (B) Thirty or 15 μg of extract proteins from the livers of two wobbler (wr/wr) mouse and two control Vps54 +/+ (+/+) littermates were resolved in contiguous lanes by SDS-PAGE. The levels of endogenous Vps54 (Top) and Vps53 (Bottom) in both groups of mice were compared by immunoblotting. The trans-Golgi p230 protein was used as loading control. (C) Quantification of Vps54 and Vps53 levels in control (+/+) and wobbler (wr) mice. Mean ± SD from three pairs of mice are shown. *, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01. (D) Vps54 levels measured by immunoblotting (15 μg/lane) in relevant tissues of wild-type and wobbler mice. (Lower) Integrated intensity profile corresponding to Vps54 band. CSC, cervical spinal cord; LSC, lumbar spinal cord. Molecular mass markers are shown on the left. Arrows indicate Vps54.