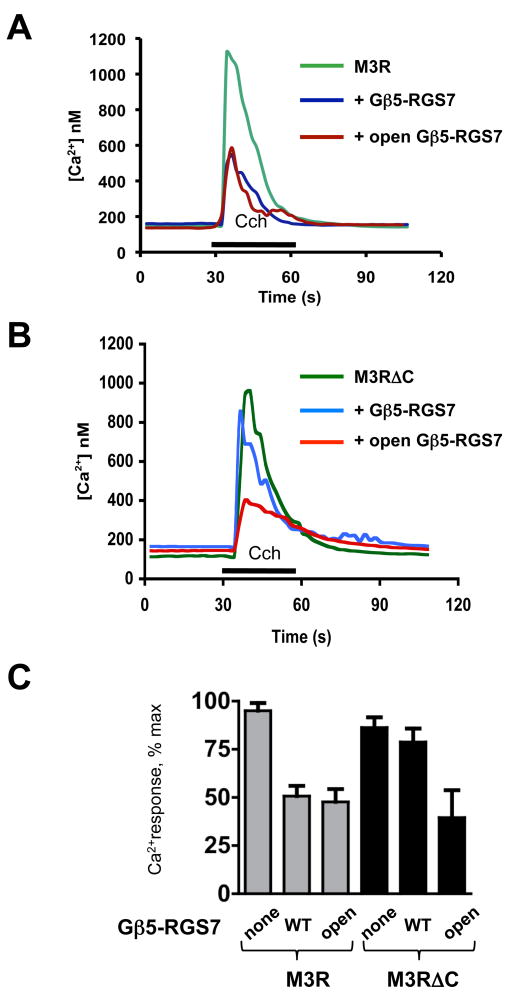
Figure 5. The C terminus of the M3R is essential for the inhibitory action of Gβ5-RGS7 on M3R signaling.
CHO-K1 cells were transiently transfected with M3R, Gβ5 and RGS7 constructs. Cells were grown on glass coverslips, then loaded with fura-2AM and mounted in a flow chamber at the stage of an inverted fluorescence microscope. Changes in free intracellular Ca2+ concentrations in response to stimulation with 100 μM carbachol were recorded in real time from the entire field which contained at least 40 cells, as described in Materials and Methods. The application of carbachol (Cch) is denoted with the black bar. (A) Representative traces from cells transfected with plasmids encoding the M3R and Lac Z cDNAs (green), the M3R together with wild-type Gβ5-RGS7 (blue) or the M3R with “open” Gβ5-RGS7 composed of RGS7 F107A/F110A and Gβ5 F284A mutants (dark red). (B) The M3R construct lacking its C-terminus (M3RΔC) was co-transfected with the wild-type or the open mutant of Gβ5-RGS7. (C). Quantification of the data from four independent experiments showing the mean ± SD of the peak Ca2+ response expressed as the percent of the maximal detected Ca2+ response. Gray bars show inhibition of full-length M3R by wild-type Gβ5-RGS7 or the open mutant, black bars represent the results with the truncated M3R mutant, M3RΔC.