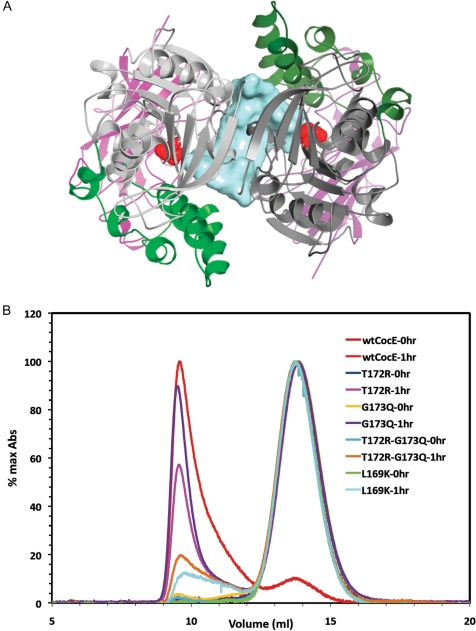
Fig. 5.
Quaternary structure of CocE. (A) X-ray crystal structure of the CocE homodimer, which is formed by a crystallographic 2-fold axis in crystals of CocE. The colors of one subunit are darker to differentiate the two monomers. The catalytic serine (S117) is shown as red spheres. A solvent-accessible channel formed at the dimer interface is colored blue. All three domains contribute to the dimer interface, which features a continuous β-sheet formed by symmetry-related strands in Domain I. (B) Size exclusion chromatography analysis of CocE and its mutants. Wild-type (wt-CocE) and mutant CocE (as indicated) were analyzed before and after incubation at 37°C for 1 h. Heat treatment leads to forms of CocE that elute in the void volume of the column, whereas non-treated CocE elutes as an apparent homodimer of molecular weight of ∼140 kDa.