Figure 4. Specific genome elements guiding neutrophil cell fate in fractal manner.
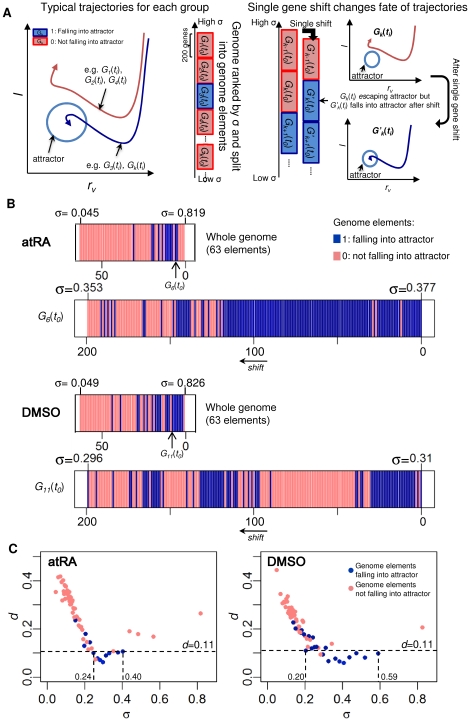
(A) Sensitivity of genome elements falling to the attractor against standard deviation: left panel, schematic trajectories of genome elements, 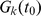 (k = 1,…,63), into (blue) and not into attractor (red), sorted by standard deviation σ. Right panel, schematic of genome element with single-gene shift can change its fate to the attractor. Illustration shows the process of single-gene shift, i.e., removing the highest σ gene from an element
(k = 1,…,63), into (blue) and not into attractor (red), sorted by standard deviation σ. Right panel, schematic of genome element with single-gene shift can change its fate to the attractor. Illustration shows the process of single-gene shift, i.e., removing the highest σ gene from an element 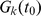 not falling into attractor, and adding the highest σ gene of the next lower rank group
not falling into attractor, and adding the highest σ gene of the next lower rank group 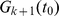 , creates a new genome element,
, creates a new genome element, 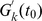 , that fall into the attractor. (B) Upper panels: the binary sequence of 63 genome elements atRA and DMSO responses represented by blue and light red, for 1 and 0 respectively. Lower panels, binary sequence of 199 additional genome elements were created using single-gene shift as in (A) for
, that fall into the attractor. (B) Upper panels: the binary sequence of 63 genome elements atRA and DMSO responses represented by blue and light red, for 1 and 0 respectively. Lower panels, binary sequence of 199 additional genome elements were created using single-gene shift as in (A) for 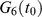 for atRA and
for atRA and 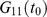 for DMSO. (C) Euclidean distance d, between the whole genome's trajectory and each genome element's trajectory. More than 50% of genome elements that fell into the attractor are close to the minimum distance (d<0.11, indicated by a dotted line).
for DMSO. (C) Euclidean distance d, between the whole genome's trajectory and each genome element's trajectory. More than 50% of genome elements that fell into the attractor are close to the minimum distance (d<0.11, indicated by a dotted line).