Figure 2.
Mutation of the major N-glycosylation site of pIgR hinders its constitutive apical transcytosis.
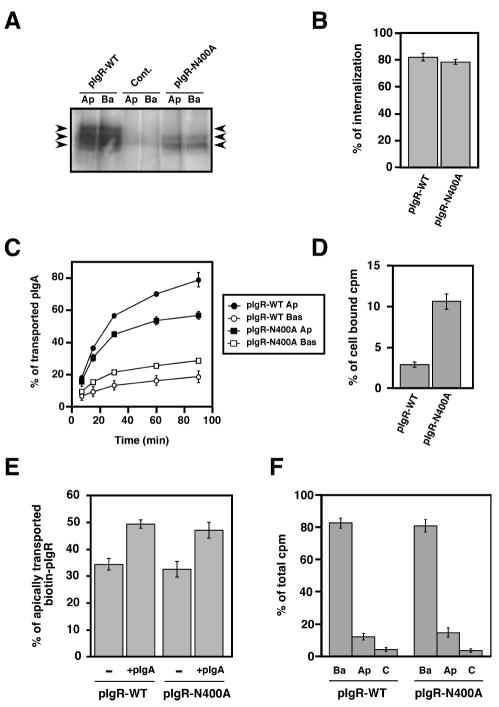
A) Apical (Ap) or basolateral (Ba) cell surface biotinylation of untransfected MDCK control cells (cont.) and cells expressing either the pIgR-WT or the mutated pIgR-N400A. The arrows point to the three major bands immunoprecipitated using the sheep anti-rabbit pIgR antibody from pIgR-WT expressing cells. The control cells were not transfected with rabbit pIgR. The pIgRN400A mutant is found as a doublet with a majority of the protein visualized as the lowest band demonstrating its weak glycosylation. The highest of the three bands is not seen with the pIgRN400A mutant, indicating that this highest band is the result of glycosylation at the N400 site.
B) Basolateral endocytosis of iodinated pIgA at 5 min mediated by the pIgR-WT and pIgR-N400A. The experiment was performed twice in triplicate, and data from both experiments were combined. Values are mean ± SD.
C) Apical transcytosis and basolateral recycling of iodinated pIgA endocytosed from the basolateral surface of MDCK cells expressing pIgR-WT or pIgRN400A. The experiment was performed three times in triplicate and one representative experiment is shown.
D) Percentage of pIgA remaining in the cells at the end of the 90 min chase of the experiment presented in C).
E) PIgA-stimulated transcytosis of pIgR-WT and pIgR-N400A. The experiment was performed four times in triplicate, and data from all experiments were combined. Values are mean ± SD. For each cell line, data were compared between +/- pIgA by using a paired Student’s t-test. We determined a statistically significant difference with p<0.01 for both pIgR-WT and pIgR-N400A.
F) Apical (Ap) and basolateral (Ba) cell surface delivery of pIgR-WT and pIgR-N400A. The experiment was performed three times in triplicate, and one representative experiment is shown.