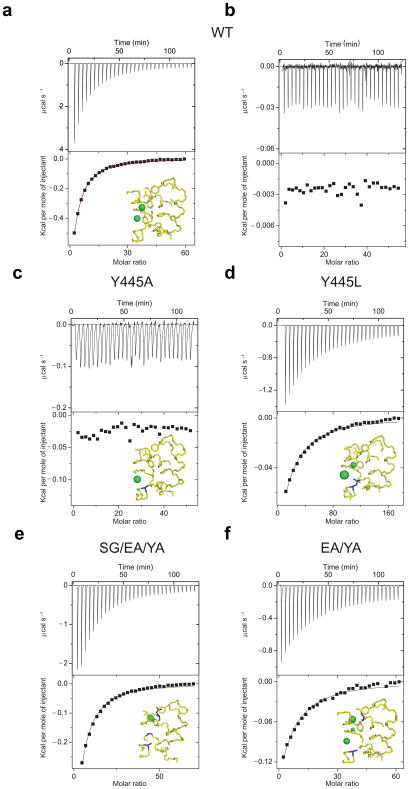
Figure 2.
Cl− binding to WT and mutant CLC-ec1. Top panels: heat liberated when KCl is titrated into the experimental chamber containing buffer and protein. The concentration of the KCl stock used was 25 mM for WT CLC-ec1, Y445A, S107G/E148Q/Y445A and E148A/Y445A mutants and 25–75 mM for the Y445L mutant. Each downward deflection corresponds to one injection. Bottom panels: the area underneath each deflection is integrated and represents the total heat exchanged (squares). Black lines are the best fits to a single site binding isotherm. (a) WT CLC-ec1. In the bottom panel the red line represents the fit to a binding isotherm with two identical sites. (b) KIsethionate binding to WT CLC-ec1. Cl− binding to the following mutants: Y445A (c), Y445L (d), S107G/E148A/Y445A (e) and E148A/Y445A (f). Insets show the structure of the ion binding site with the mutated residue(s) highlighted in blue. The structure of the S107A/E148Q/Y445A mutant is used as a model for the S107G/E148A/Y445A mutant. Green spheres represent bound Cl− ions. Following the published convention 27, the spheres occupying Scen in the Y445L and E148A/Y445A mutants are scaled down in size to reflect the reduced anion occupancy of this site in these mutants. (PDB accession codes: WT: 1OTS, Y445A: 2HTK, Y445L: 2HT3, S107A/E148Q/Y445A:2EZ0 and E148A/Y445A: 3DET)