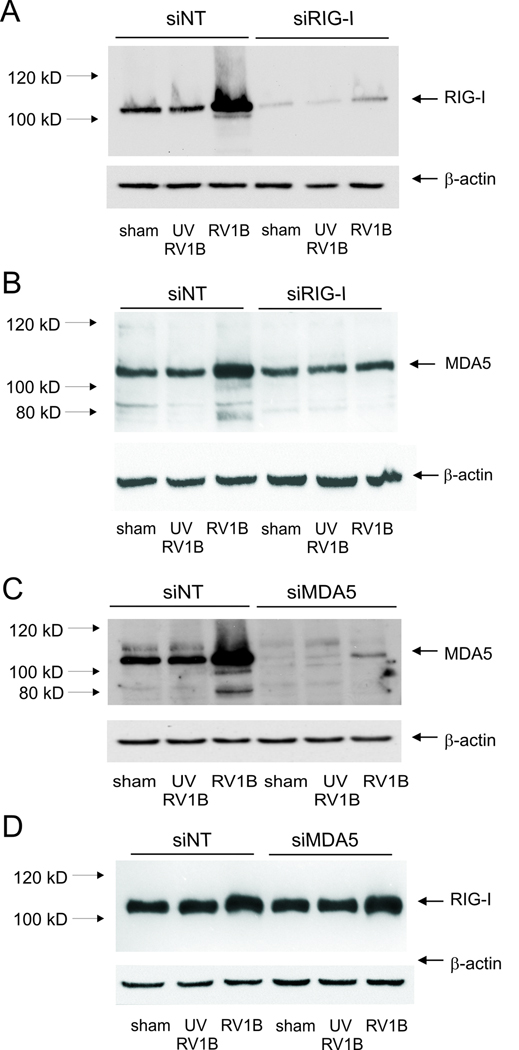
Figure 4. RIG-I and MDA-5 siRNA knockdown efficiencies.
A, B. RIG-I or non-targeting siRNA was transfected into BEAS-2B cells. After transfection, cells were infected with RV1B, UV-irradiated RV1B (UV-RV1B) or sham. After infection, cell lysates were probed with antibodies against RIG-I (A) or MDA-5 (B). Note the inductions in RIG-I and MDA5 expression with intact RV, as well as the apparent degradation of MDA-5 following viral infection. C, D. MDA5 or non-targeting siRNA was transfected into BEAS-2B cells. After transfection, cells were infected with RV1B, UV-irradiated RV1B (UV-RV1B) or sham. After infection, cell lysates were probed with antibodies against either MDA5 (C) or RIG-I (D). (The blots shown are a representative of three separate experiments.)