Figure 1.
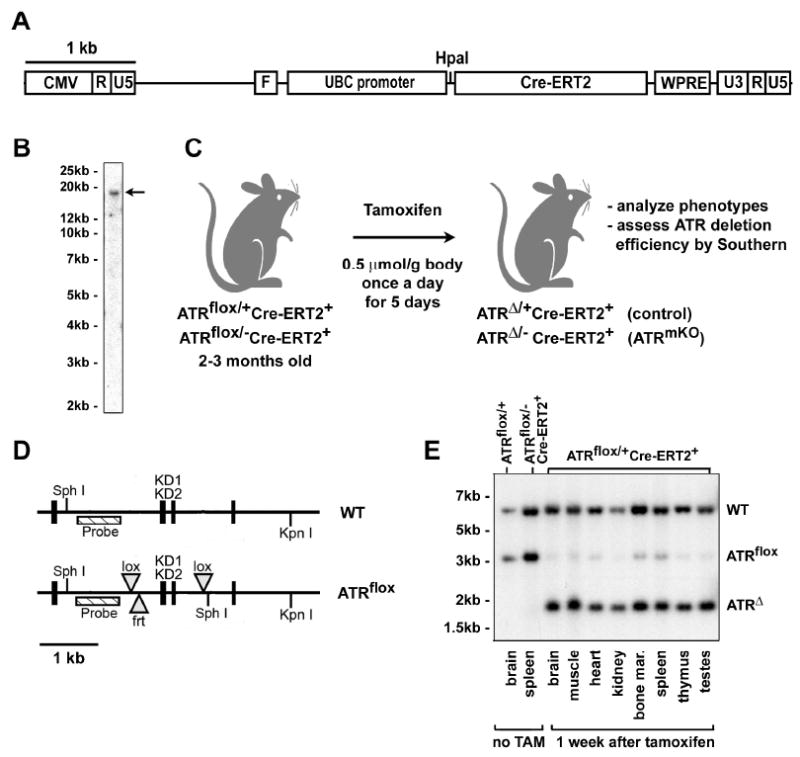
A drug-inducible system to delete ATR in adult mice. (A) Lentiviral construct used to generate Cre-ERT2 fusion protein-expressing lentivirus. (B) A founder with a single copy integrant that expressed high levels of Cre-ERT2 was chosen to establish Cre-ERT2 lentitransgenic mouse line (arrow). (C) TAM treatment regimen used to stimulate recombination of the ATRflox allele. Mice were treated TAM at 2-3 months of age by oral gavage or intraperitoneal injection and analyzed subsequently at various time points. (D) Schematic of the ATRflox region (Brown and Baltimore, 2003). The kinase domain-encoding exons (KD1 & KD2) and probed region are shown. The null allele of ATR (ATR-) is wild-type in this probed region. (E) Southern blot of genomic DNA isolated from TAM-treated ATRflox/+Cre-ERT2+ mice. DNA samples from various tissues were digested with Sph I and Kpn I, Southern blotted and detected for the ATRflox region using the probe indicated in (D). Sph I ATRflox allele fragment = 3.1 kb, Sph I ATRΔ allele fragment = 1.8 kb.
