Figure 4.
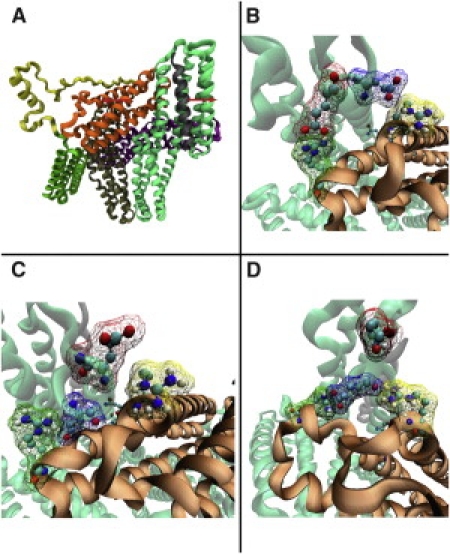
Helical bundle conversion in full-length vinculin. (A) The vinculin-VBS complex that was formed using structural information from PDB 1TR2 and PDB 1T01. Binding to VBS causes local conformational changes in D1. Two helical regions in D1 are pushed apart while VBS is inserted in between. Three sets of electrostatic interactions exist between D1 and Vt: 1), E29-R945 and E31-R1008; 2), E14-K996; and 3), R7-E986. Insertion of VBS causes changes in the electrostatic interactions mainly in set 1. (B) Electrostatic interactions in set 1 before VBS binding: E29 interacts with R945, and E31 interacts with R1008. (C) Set 1 after VBS complex formation and minimization. After rearrangement from VBS binding, E31 interacts with R945, and E29 interacts with R1008. (D) The interaction in set 1 rearranges once again after an equilibration for 100 ps. The E29 now interacts with both R945 and R1008, and E31 is no longer paired. 1), E29 and E31 with R945 and R1008; 2), E14 with K996; and 3), E7 with E986.
