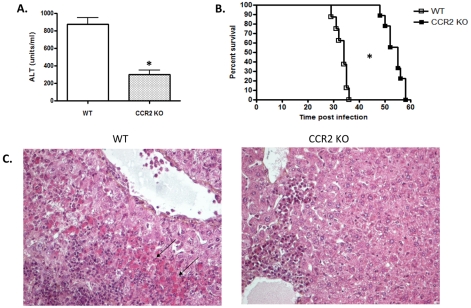
Figure 5. Absence of CCR2 signaling reduces liver pathogenicity and prolongs survival of T. brucei infected mice.
A) Serum ALT levels were measured in WT and CCR2 KO mice on day 28 of infection (mean ± SEM of three individual mice of one of two independent experiments performed). *, significantly (p<0.05) lower compared to WT mice. B) Survival time of infected WT and CCR2 KO mice. Data are representative of one of two independent experiments performed. *, significantly longer (p<0.05) compared to WT mice. C) Microscopic examination (H&E staining; magnification ×100) of liver sections from WT and CCR2 KO mice on day 28 of infection (representative of 3 animals tested). In CCR2 KO mice hepatocyte necrosis is low, whereas in WT mice important hepatitis and fields of necrosis are observed (arrows).