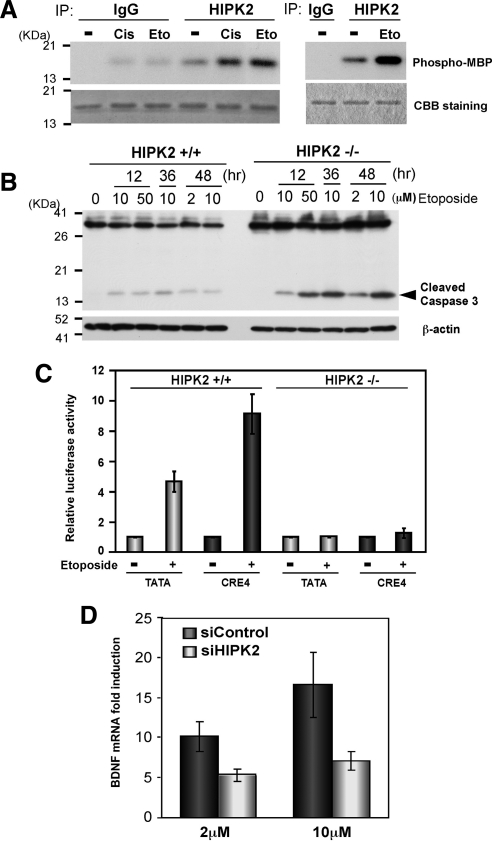
Figure 7.
Etoposide induces CRE-dependent transcription and BDNF mRNA via HIPK2. (A) FlagHIPK2-transfected K562 cells were treated with 0.5 μg/ml cisplatin or 50 μM etoposide for 6 h and harvested for immunoprecipitation with anti-HIPK2 antibody or control IgG. The immunoprecipitates from two independent experiments were incubated with recombinant MBP at 30°C for 30 min (left) or 22°C for 4 min (right) in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP and loaded on SDS-PAGE. Phosphorylated MBP was detected by autoradiography (top). Comparable protein loading was verified by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining (bottom). (B) Twenty-four hours after plating 5 × 106 HIPK2+/+ or −/− MEF cells, they were treated with indicated concentrations of etoposide for 12, 36, or 48 h. Whole cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Caspase 3 antibody. β-actin Western blot is shown as a loading control. (C) HIPK2+/+ or −/− MEF cells were transfected with TATA-luciferase or CRE4-luciferase and incubated for 24 h. Then cells were treated with 10 μM etoposide for 48 h and harvested for luciferase assay. Luciferase expression with each reporter without etoposide treatment was set to 1.0, and mean values from five independent experiments are shown; error bars, SEs. (D) 1 × 107 SH-SY5Y cells were transfected with nontargeting (siControl) or HIPK2-targeting (siHIPK2) siRNA and incubated for 24 h. Cells were then treated with 2 or 10 μM etoposide for 48 h for RNA isolation. BDNF exon III mRNA expression was analyzed with quantitative real-time PCR. BDNF mRNA expression in nontreated cells was set to 1.0; mean values from five independent experiments are shown; error bars, SEs.