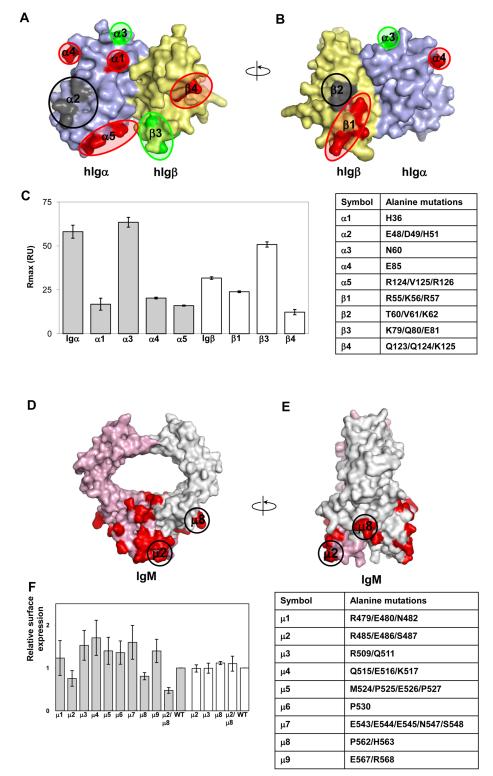
Figure 5.
Binding of mutant human Igα and Igβ to recombinant human Cμ2-Cμ4. (A)Surface representation of human Igαβ heterodimer model. Point mutations resulting in reduction or increase of binding circuled red and green, respectively. Mutations causing absence of protein expression are circled black. Alpha and beta chains of Igαβ heterodimer are colored pale blue and yellow, respectively. (B) 180 degree rotation of the previous view of the Igαβ heterodimer model. (C) Binding of Igα (grey bars) and Igβ (white bars) mutants to Cμ2-Cμ4. Mutant concentration in the analyte was kept constant at 4μM. At least three sets of experiment were performed for each mutant. A table with mutant description is given for reference. (D) Structural model Cμ3-Cμ4 domains of IgM. IgM chains are painted pink and grey with groups of amino acid selected for mutations in red. Groups of mutations μ2 (R485, E486, S487) and μ8 (P562, H563) that affect IgM surface expression are circled. Arginine 485 and proline 562 are highly concerved in IgM. (E) 90 degree rotation of the previous view. (F) Relative surface expression of different IgM groups of mutants (grey bars); white bars represent relative surface expression for IgM YS/VV construct. The YS/VV mutation in transmembrane domains of IgM allows surface IgM expression without binding to the Igαβ heterodimer. That indicates that the effects of the mutations were likely through disrupting interactions with Igαβ. A table with mutant description is given for reference. See also Figure S5.