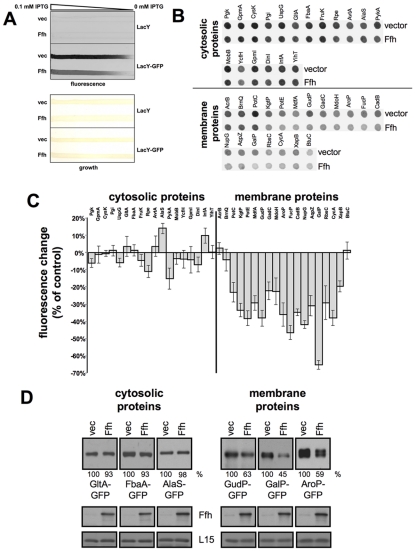
FIG 2 .
Effect of Ffh overexpression on expression of cytosolic and membrane proteins. (A) For a control experiment, we used E. coli cells expressing chromosomally encoded LacY-GFP or LacY as indicated and harboring plasmids encoding arabinose-inducible Ffh or carrying empty vector. The transformants were grown overnight on a nylon membrane covering an LB agar plate containing a linear concentration gradient of IPTG (0 to 0.1 mM) for LacY or LacY-GFP induction and 0.02% arabinose for Ffh induction. The upper panel shows the fluorescence as recorded using Typhoon. The lower panel shows the bacterial growth on the nylon membrane. (B) E. coli cells harboring plasmids carrying arabinose-inducible ffh or empty vector were transformed with vectors encoding the indicated GFP hybrids. The cells were grown overnight on LB agar plates covered with nylon membranes and supplemented with 0.02% arabinose. The fluorescence levels of the colonies on the nylon membrane were recorded (B) and quantified (C). The experiment was repeated nine times, and the error bars represent the standard deviations. (D) Cells harboring a plasmid encoding arabinose-inducible Ffh or carrying an empty vector were transformed with a second plasmid encoding either of the indicated GFP hybrids and grown in LB broth with 0.2% arabinose. After disruption, equal amounts of total proteins from each extract were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-GFP and anti-Ffh antibodies. As a loading control, antibodies against the ribosomal protein L15 were used. The proteins’ expression levels were quantified and are shown as percentages of their expression levels in samples with empty vector. The experiments were repeated three times, and the results shown are representative, with standard deviations that did not exceed 10%.