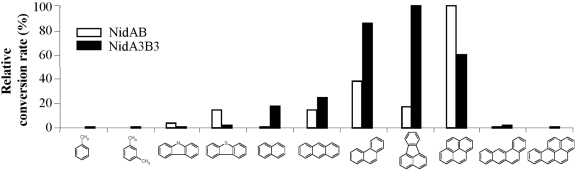
FIG 2.
Diagram showing substrate preference by NidAB and NidA3B3, indicating that pyrene and fluoranthene were the most effective aromatic substrates, respectively, for these two enzymes. The relative conversion rate for each aromatic substrate is the sum of all metabolites produced, regardless of hydroxylation positions. The rates of pyrene and fluoranthene conversion were set at 100% for NidA and NidA3, respectively, and other substrates were calculated relative to the rates of pyrene and fluoranthene conversion. Biotransformation assays were conducted at least two times, and only representative results are shown as relative conversion rates. The chemical structures and compound names are shown in Fig. 3.