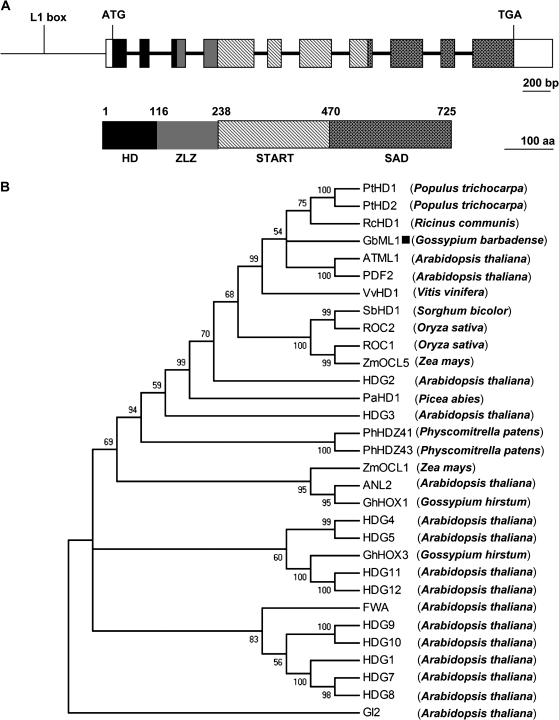
Fig. 1.
Molecular characterization of GbML1. (A) (Top) Genomic structure of GbML1. Exons are represented in boxes, and intron positions are indicated by bold lines. The promoter region is represented by a narrow line and the L1 box position is indicated. (Bottom) The HD domain is indicated by a black box (aa: 1–115), the ZLZ domain (aa: 116–237) is indicated by a grey box, the START domain is filled with dashed lines (238–469), the SAD domain is filled with stars (aa: 470–725), and the untranslated regions are indicated by empty boxes. The bar for the nucleotide represents 200 bp while the bar for the protein represents 100 aa. (B) Phylogenetic tree showing the relationship between GbML1 and other HD-Zip IV proteins. The tree presented here is a Neighbor–Joining tree based on amino acid sequence alignment. The numbers next to each node give bootstrap values for 1000 replicates. Alignments are derived from the following sources: Gossypium barbadense GbML1 (this study), Gossypium hirsutum GhHOX1 (AF530913) and GhHOX3 (AY626159), Arabidopsis thaliana ATML1 (U37589), PDF2 (AB056455), GL2 (Z54356), ANL2 (AF077335), FWA (AAG09302), HDG1 (AJ224338), HDG2 (AC000098), HDG3 (AC005700), HDG4 (Z97344), HDG5 (AB013394), HDG7 (AB025603) HDG8 (AC012328), HDG9 (AB005238), HDG10 (AC007894), HDG11 (AC012396), and HDG12 (AC034106), Populus trichocarpa PtHD1 (CM000340) and PtHD2 (CM000347), Vitis vinifera VvHD1 (CU459396), Ricinus communis RcHD1 (EQ973828), Zea mays ZmOCL1 (Y17898) and ZmOCL5 (AJ250987), Sorghum bicolor SbHD1 (CM000765), Oryza sativa ROC1 (AB077993) and ROC2 (AB101645), Picea abies PaHD1 (AF172931), Physcomitrella patens PhHDZ41 (BK005813) and PhHDZ43 (BK005815). The GbML1 was marked with a black square.