Figure 1. Electroresponsive Membrane Properties and Morphologies of mEC Neurons.
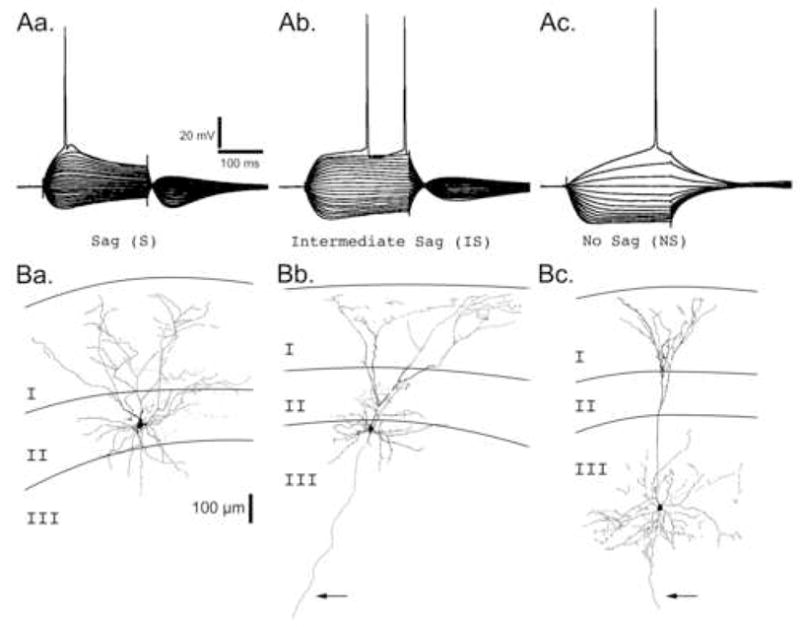
ARepresentative voltage traces from the three primary neuronal types found in Layers II and III. Neurons were recorded in current clamp mode and injected with a holding current sufficient to maintain the membrane potential at −70 mV. Neurons were then hyperpolarized or depolarized by square current steps ranging from −300 pA to > +300 pA in 30 pA intervals. Neuronal types are primarily classified by the degree of “sag” in their membrane potential in response to a sustained hyperpolarizing current injection: Aa. Sag (S), Ab. Intermediate Sag (IS), and Ac. No Sag (NS). Scale bars associated with Sag (S) neuron apply to all voltage traces. B. Camera lucida reconstructions of representative biocytin filled neurons for each neuron class in the superficial layers of the mEC. Layers I, II, and III are indicated. Arrows point to axons extending into the deep layers of the mEC. Ba. A Sag neuron with a stellate morphology whose cell body was located in layer II. Bb. An Intermediate Sag neuron with a pyramidal-like morphology whose cell body was located on the border of layers II and III. Bc. A No Sag neuron with a pyramidal morphology whose cell body was located in layer III. Scale bar (100 μm) associated with the layer II stellate neuron applies to all neurons.
