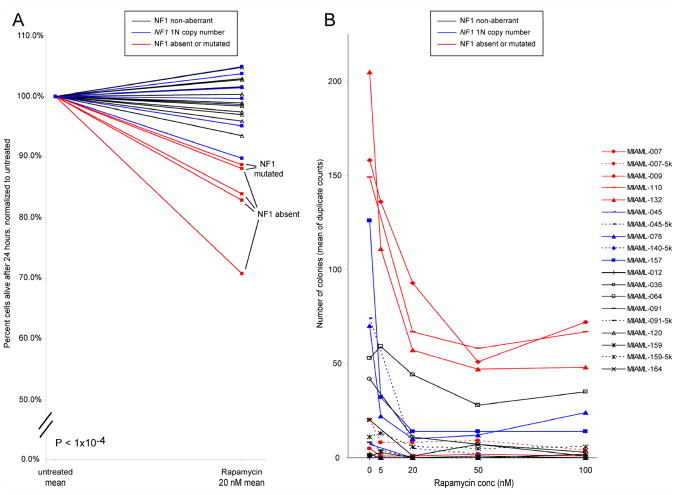
Figure 4. Sensitivity of NF1 null AML blasts to rapamycin-induced apoptosis and inhibition of colony formation of CD34+/CD38− cells by rapamycin.
A: AML blasts from AML cases with wild type NF1 (N=12; black), NF1 mono-allelic loss but preserved NF1 expression from the retained allele (N=6; blue) or NF1 null states (N=5; red) due to either NF1 mutations or absent NF1 mRNA expression were purified using negative selection and subsequently cultured for 24 hours in the presence or absence of 20nM rapamycin. Blast viability and apoptosis were measured using FACS-based annexin V-PI staining. Displayed are normalized viabilities of rapamycin-treated samples compared with paired untreated samples. B: CD34+/CD38− cells from AML cases with wild type NF1 (N=7; black), NF1 mono-allelic loss but preserved NF1 expression from the retained allele (N=4; blue) or NF1 null states (N=4; red) due to either NF1 mutations or absent NF1 mRNA expression were purified using FACS-sorting and 1000 cells plated in cytokine-supplemented methylcellulose in the absence or presence of escalating doses of rapamycin for 7 days. Colony counts represent means of duplicate measurements. Cases with sufficient cells were also plated at 5000 cells per well as indicated (−5k).