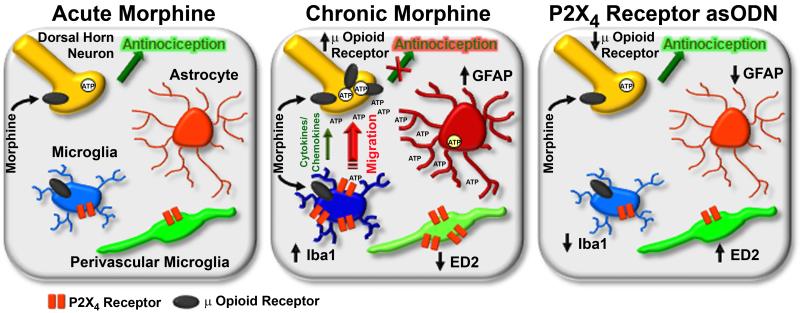
Figure 2.
P2X4 receptor asODN and naloxone attenuates morphine-induced P2X4 receptor expression. (a) Lumbar spinal cord protein from rats receiving chronic subcutaneous morphine for 0, 1, 4 or 7 days was probed for P2X4 receptor and β-actin protein expression. Quantification of fold changes of P2X4 receptor expression normalized to β-actin loading control ± SEM (n=4 or 5) is located below a representative western blot membrane. ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to naïve. (b) Day 7 lumbar spinal cord protein from naïve rats and groups receiving P2X4 receptor asODN alone, mismatch asODN plus morphine, morphine alone or P2X4 receptor asODN plus morphine was probed for P2X4 receptor and β-actin protein expression. Quantification of fold changes of P2X4 receptor expression normalized to β-actin loading control ± SEM (n=5) is located below a representative western blot membrane. †† p<0.01 compared to naïve, ‡ p<0.05 compared to P2X4 receptor asODN alone, # p<0.05 compared to morphine alone. (c) Mechanical and Thermal behavioral analgesia was measured for rats receiving subcutaneous morphine and morphine plus naloxone. ***p<0.001 compared to morphine plus naloxone and naïve. (d) Lumbar spinal cord protein from rats receiving seven days of continuous subcutaneous administration of morphine alone or morphine plus naloxone was probed for P2X4 receptor and β-actin protein expression. Quantification of fold changes of P2X4 receptor expression normalized to β-actin loading control ± SEM (n=4 or 5) is located below a representative western blot membrane. *p<0.05 compared to naïve and morphine plus naloxone.