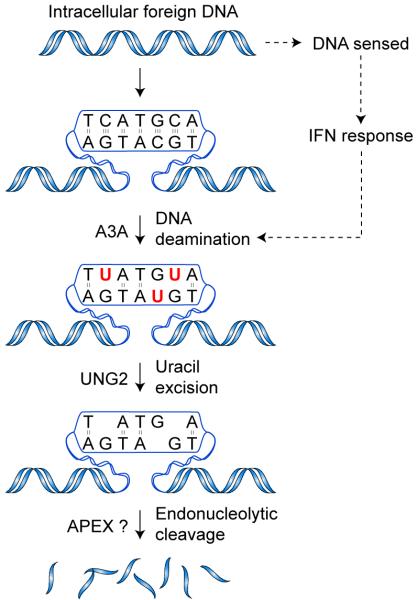
Figure 7.
A model for foreign DNA restriction. Foreign DNA enters the cell by escaping from an endosomal or phagosomal compartment, by infection, or by other means. TLR-dependent or - independent DNA sensing initiates signaling cascades that result in production of IFN, which in turn induces A3A expression. A3A engages the foreign DNA, deaminating multiple cytidines in a molecule. The resulting uracils are excised by UNG2, creating nuclease-sensitive abasic sites. Cleavage of the backbone by APEX1 or other nucleases results in fragmentation and degradation of the foreign DNA.