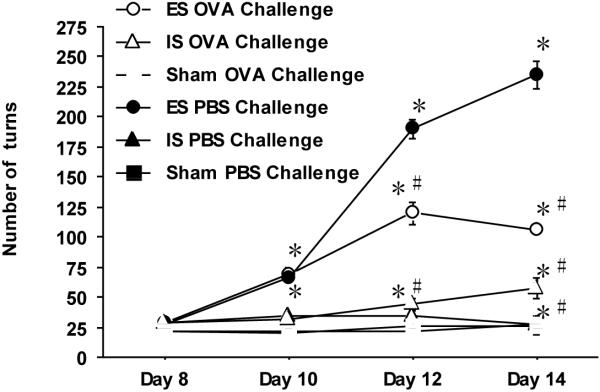
Figure 2. Provocation of airway hypersensitivity diminishes avoidance response to aversive tailshock.
The total number of wheel turns during each session of tailshock was recorded for each subject and plotted as a function of stress days during the duration of the stress paradigm. Data represents mean (n=15) ± std. error in the number of wheel turns at a given time point. (*) and (#) designates significant p ≤ 0.05) difference between each experimental group at each time point. OVA; ovalbumin-treated, PBS; Phosphate buffered saline-treated, ES; escapable stress and IS; inescapable stress, and Sham.