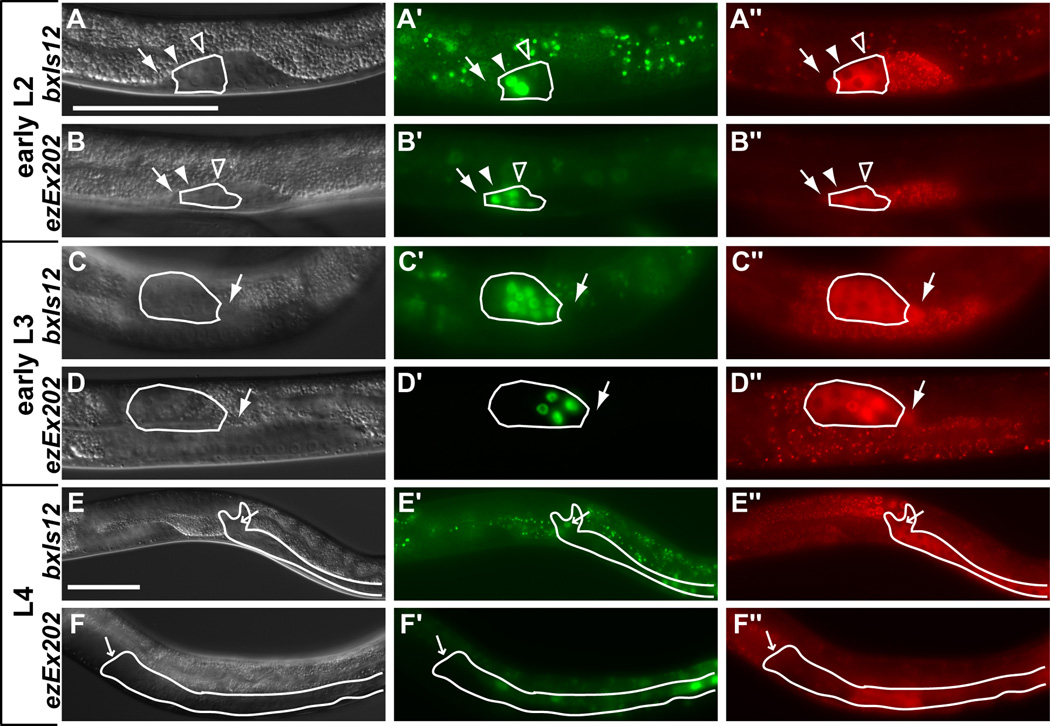
Fig. 2. egl-5 gonadal expression.
Left column: DIC images. Middle column: (A, C, E) bxIs12 (egl-5::GFP with full regulatory region) expression (Teng et al., 2004), (B, D, F) exEx202 (pAKK33-123bp regulatory region required for egl-5 gonadal expression). Right column: germ cell marker nmy-2::PGL-1::mRFP1 (red punctate expression distinguishes germ cells from somatic cells (Wolke et al., 2007)). Gonadal regions containing VD and SV cells and descendents are outlined in white (green fluorescence outside white outlines is intestinal autofluorescence). White arrows indicate the LCs, filled arrowheads indicate the VD precursors, open arrowheads indicate the SV precursors, and small white arrows in rows E and F indicate the valve cells. (A, B) In early L2 GFP expression is present in the three vas deferens (VD) precursors (strong) and four seminal vesicle (SV) precursors (weaker) (all seven cells are not in focal plane). (C, D) In early L3 as the gonad reflexes to the posterior the VD and SV cells start dividing. GFP expression remains strong in VD daughters and proximal SV daughters and is much weaker in distal SV daughters. (E) In L4 as the VD and SV daughters terminally differentiate GFP expression is retained only in the four valve cells. (F) Expression is occasionally present in the valve cells of late L4 larvae and adults. Scale bars = 50µm.