Figure 4.
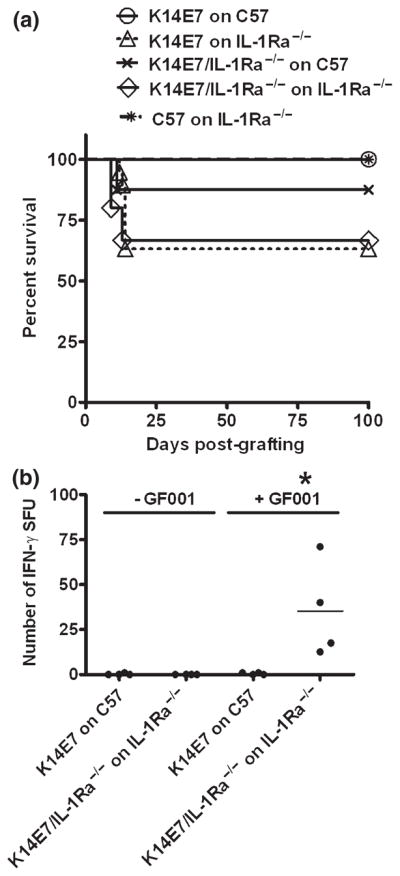
Loss of IL-1Ra leads to spontaneous K14E7 graft rejection (a) Wild-type K14E7 skin grafts were placed on naïve C57BL/6 recipients (○; n = 12) or IL1-Ra−/− recipients (△; n = 19, P = 0.020 compared to wild-type graft). Alternatively, K14E7 grafts deficient in IL-1Ra were placed on naïve C57BL/6 recipients (x; n = 8, P > 0.05) or IL1-Ra−/− recipients (◇; n = 15, P = 0.030). Non-transgenic C57BL/6 skin was placed on IL-1Ra−/− as a negative control graft ( ; n = 8). A Kaplan–Meier analysis of graft survival over time is plotted. (b) E7-specific CD8+ T cells in K14E7-grafted animals with or without IL-1Ra. Splenocytes from graft-primed animals were analysed at day 21 postgrafting for the ability to respond to E7 peptide (GF001) by overnight IFN-γ ELISPOT in the presence (+GF001) or absence (−GF001) of peptide. Data represent individual animals assessed in independent experiments.
; n = 8). A Kaplan–Meier analysis of graft survival over time is plotted. (b) E7-specific CD8+ T cells in K14E7-grafted animals with or without IL-1Ra. Splenocytes from graft-primed animals were analysed at day 21 postgrafting for the ability to respond to E7 peptide (GF001) by overnight IFN-γ ELISPOT in the presence (+GF001) or absence (−GF001) of peptide. Data represent individual animals assessed in independent experiments.
