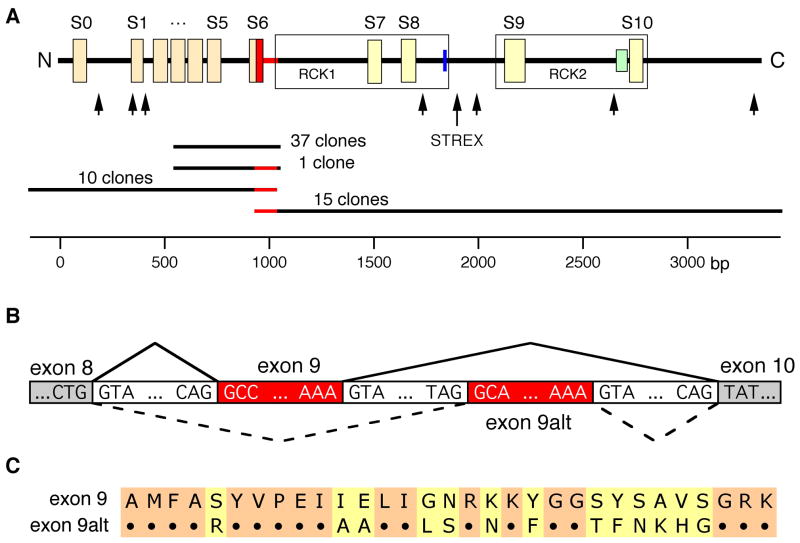
Fig 1.
Identification of splice products of slo1 in human LNCaP cells. (A) upper panel: schematic view of hSlo1 structural elements: S0–S10 – hydrophobic domains; RCK1 and RCK2 regions (boxed); heme-binding site (blue); Ca2+-bowl (green). Arrows designate sites of alternative splicing identified in mammalian slo1 mRNAs. Region corresponding to exon 9 is highlighted in red. Lower panel: clones used to identify transcripts with e9alt (red). Nucleotide positions according to hslo1 mRNA sequence U11058 are shown on the scale. (B) Schematic overview of the novel alternatively spliced exon 9 in hslo1 form LNCaP cells. (C) Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of slo1 exon 9 and exon 9alt (for nucleotide sequence see suppl. Fig 2).