Figure 8. Functional hyperemia mediated by mGluR and glutamate uptake is controlled by separate pathways.
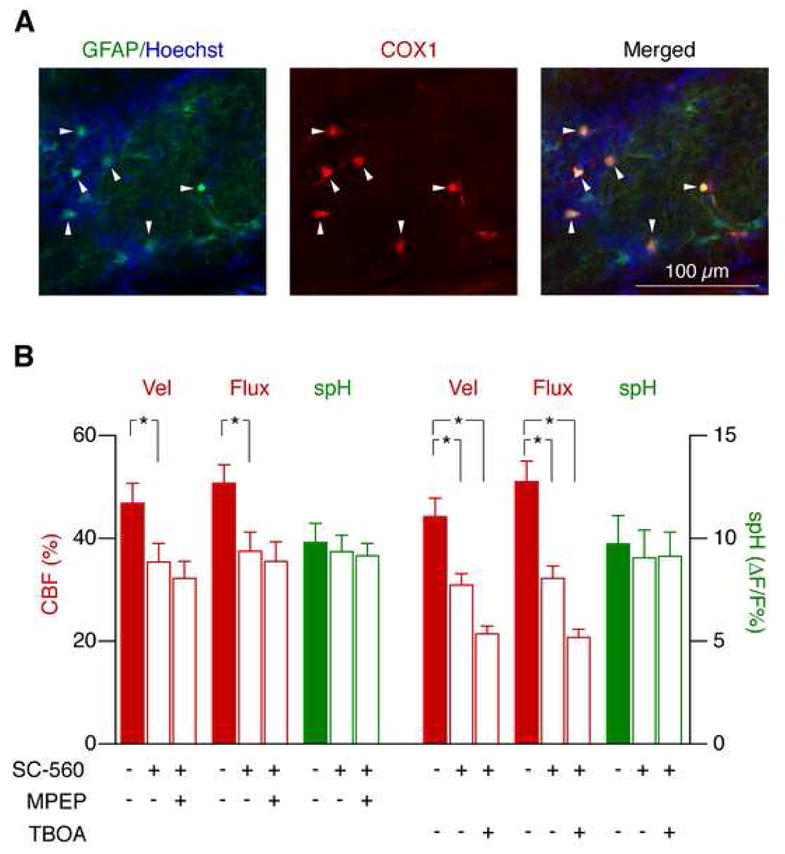
(A) COX1 is exclusively expressed by astrocytes in the glomerular layer. GFAP-GFP mice were used to identify astrocytes (green). Glomeruli were identified as cell-poor areas surrounded by juxtaglomerular cells (Hoechst 33258, blue). COX1 (red) was only detected in astrocytes (merged images, right).
(B) Functional hyperemia mediated by mGluR5, but not by glutamate uptake, depends on COX1 activation. SC-560 reduced the odor-evoked CBF response. Application of MPEP after SC-560 had no additional effect, indicating that mGluR5 affects CBF predominantly through COX activation. In contrast, TBOA reduced functional hyperemia even further after SC-560 application (mean ± s.e.m., *p < 0.05, Repeated Measures ANOVA followed by Tukey Test).
