Figure 3.
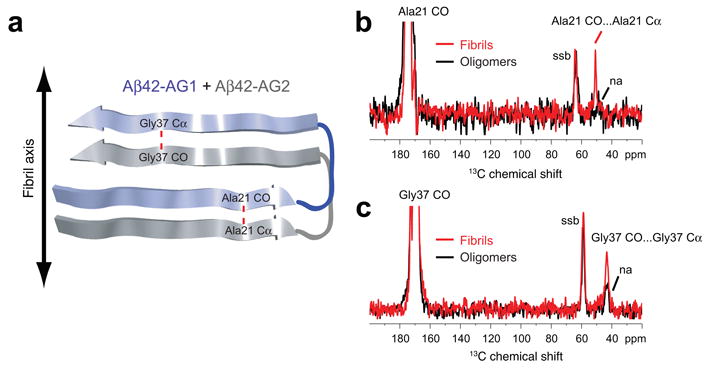
Parallel and in-register orientation of β-strands in Aβ42 fibrils. (a) Labeling scheme to test for parallel and in-register orientations of the N- and C-terminal β-strands in Aβ42 fibrils and oligomers using an equimolar mixture of Aβ42-AG1 and Aβ42-AG2 peptides. The red dashed line corresponds to the 4.7 Å distance expected between adjacent Ala21 residues and adjacent Gly37 residues along the fibril axis. (b) Rows through the Ala21 13CO diagonal resonance in DARR NMR spectra of Aβ42 fibrils (red trace) and oligomers (black trace). A distinct Ala21 13CO… Ala21 13Cα cross-peak is observed in the fibril conformation, but not the oligomer conformation. (c) Rows through the Gly37 13CO diagonal resonance in DARR NMR spectra of Aβ42 fibrils (red trace) and oligomers (black trace). A distinct Gly37 13CO… Gly37 13Cα cross-peak is observed in the fibril conformation, but not in the oligomer conformation. Smaller natural abundance (na) cross-peaks are observed in the oligomer samples. Spinning side bands (ssb) due to magic angle spinning are indicated. The data indicate that Aβ42 fibrils have β-strands in a parallel and in-register orientation, but oligomers do not.
