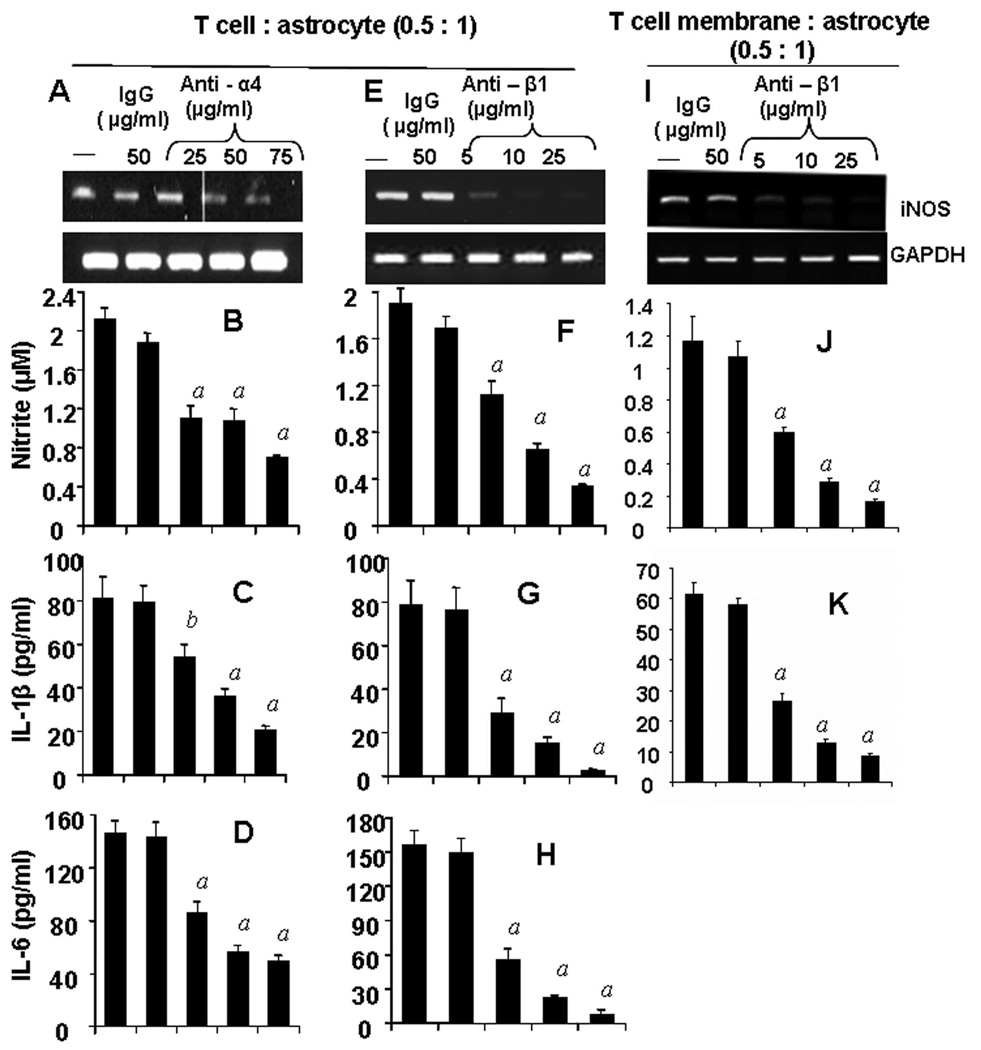
Figure 3. Functional blocking antibodies against either α4 or β1 chain of VLA-4 inhibit the ability of female MBP-primed T cells to induce the expression of proinflammatory molecules in primary mouse astroglia via cell-to-cell contact.
MBP-primed T cells were mixed with either different concentrations of antibodies against the α4 (A – D) or β1 (E – H) chain of VLA-4 or control IgG and rocked gently for 1 h at room temperature. Cells were centrifuged, washed twice, and added to astroglia at a ratio of 0.5:1 T cell:glia. After 1 h of stimulation, culture dishes were shaken and washed to lower T cell concentration. (A & E), Adherent astroglia were incubated in serum-free media for 5 h and expression of iNOS was analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (A & E). After removal of T cells, adherent astroglia were incubated in serum-free media for 23 h and supernatants were used to assay nitrite (B & F), IL-1β (C & G) and IL-6 (D & H) as described in “Materials and Methods”. Plasma membranes of MBP-primed T cells were mixed with different concentrations of antibody against the β1 chain of VLA-4 or control IgG for 1h, washed and added to astroglia. After 6 h of incubation, expression of iNOS in astroglia was analyzed by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (I) and after 24 h of incubation, supernatents were used to assay nitrite (J) and IL-1β (K). Data are mean ± S.D. of three different experiments. a p < 0.001 vs. MBP-primed T cells only; b p < 0.05 vs. MBP-primed T cells only.