Figure 5.
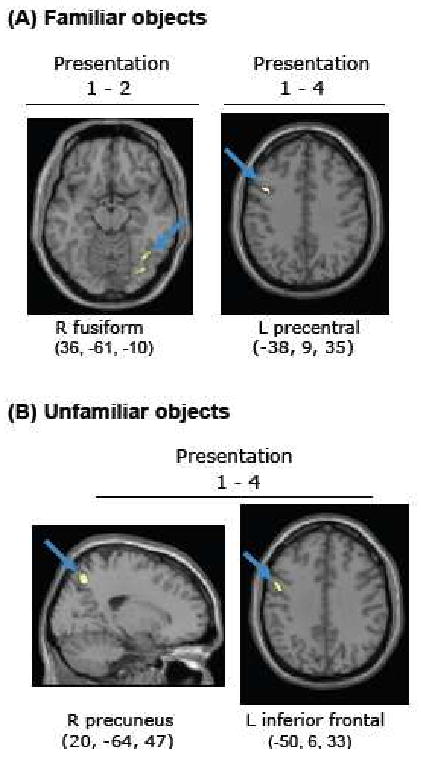
Brain regions where the magnitude of repetition suppression (thresholded at p < 0.001) for familiar (A) and unfamiliar (B) objects was modulated by reaction time priming on a within-subjects basis are displayed. For familiar objects, we detected voxels in the right fusiform gyrus (A, left panel) where repetition suppression from presentation 1 to 2 correlated with priming at presentation 2 across subjects (at p < 0.05) and within subjects (at p < 0.05), combined probability p < 0.0000025. From presentation 1 to 4, repetition suppression in the left precentral gyrus (A, right panel) correlated with priming of familiar objects (at p < 0.005) and repetition suppression in the right precuneus (B, left panel) and left inferior frontal gyrus (B, right panel) correlated with priming of unfamiliar objects (at p < 0.005).
