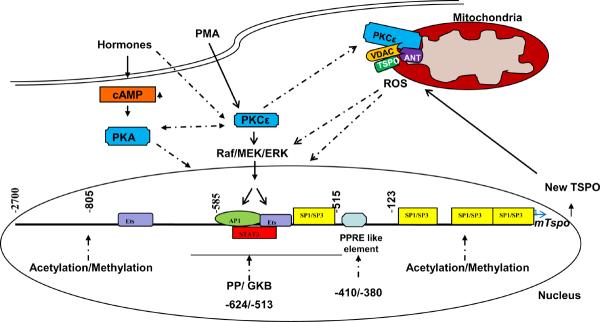
Figure 1.
Hypothetical model for transcriptional regulation of Tspo in hormone- and cAMP- responsive MA-10 Leydig cells, and non-responsive NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. Data presented in this review identified PKCε as the key regulator of Tspo expression. Activation of PKCε, mediated through a MAPK-ERK pathway, targets the AP-1, Ets, and STAT3 transcription factors, whose binding sites are localized to the −805/−515-bp region upstream of the Tspo transcription start site. Ets and Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors play a major role in basal Tspo transcription, and epigenetic modifications of Tspo may also play a role in its expression. Upon activation, PKCε is translocated to the outer mitochondrial membrane, where it interacts with the two primary TSPO-associated proteins VDAC and ANT. Cross-talk between PKC and cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) is possible. Known interactions are denoted by solid lines and hypothetical pathways are denoted by dotted lines.