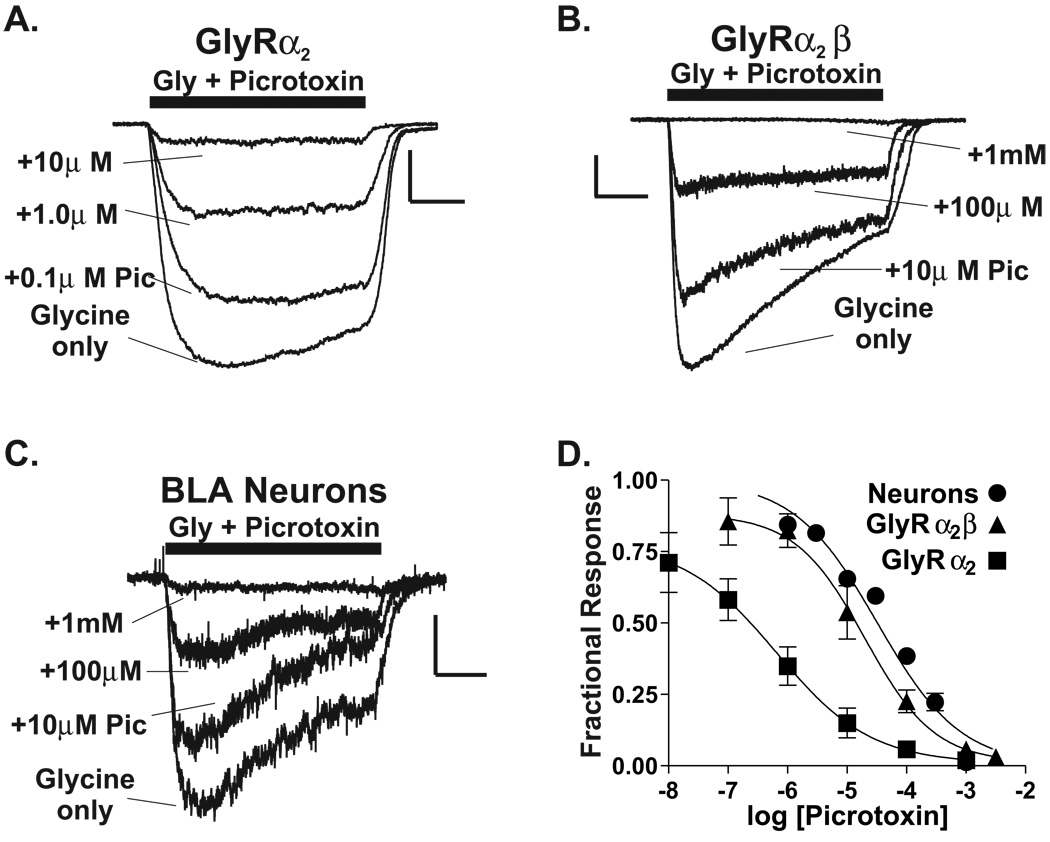
FIGURE 5.
The picrotoxin sensitivity of native BLC glycine receptors is similar to α2/β channels expressed in a heterologous system. (A) Picrotoxin sensitivity of glycine-gated currents from a L-cell transfected with rat GlyRα2 expression construct (see Methods). For all traces, an EC50 concentration of glycine was used. Note that co-application of 10µM picrotoxin with glycine inhibited the current >90% when compared to glycine alone. Calibration bars: x = 1 second; y = 0.3nA. (B) Picrotoxin sensitivity of glycine currents from a L-cell transfected with both rat GlyRα2 and rat GlyRβ expression constructs. Note that 10µM picrotoxin inhibited only ~25% of the current. Calibration bars: x = 1 second; y = 0.2nA. (C) Picrotoxin sensitivity of glycine currents in acutely dissociated adult rat BLC neurons. Note that 10mM picrotoxin inhibited ~24% of the glycine current. Calibration bars: x = 1 second; y = 0.15nA. (D) Picrotoxin concentration-response relationships for L-cells expressing rat GlyRα2, rat GlyRα2 + β, and native BLC glycine receptors. The IC50 for picrotoxin for a2/β-expressing cells was 200µM (Hillslope = −0.74, n = 4) and was similar to that determined for native receptors (IC50 = 320µM, Hillslope = −0.62, n = 3–9). In contrast, GlyRα2 homomeric channels were substantially more sensitive to picrotoxin with an IC50 = 0.7µM (Hillslope = −0.55, n = 4–8).