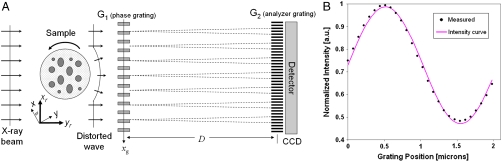
Fig. 1.
Working principle of the grating interferometer. (A) Through the Talbot effect, a periodic interference pattern is formed behind the phase grating (G1), in the plane of the analyzer grating (G2) (17). (B) Plot of the intensity oscillation (shifting curve) as a function of the grating position xg for a detector pixel over one period of the analyzer grating. The dots correspond to the measured values (normalized to unit) while the gray line shows a sinusoidal fit.