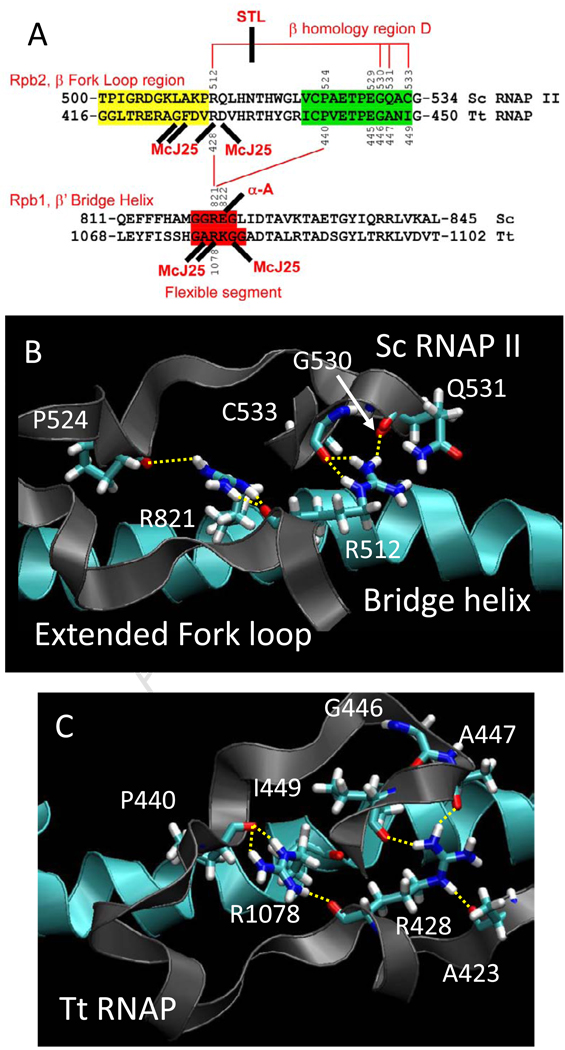
Fig. 2.
Conformational coupling between the bridge α-helix and the extended fork loop region. A) Summary of sequences, proposed interactions and interactions with inhibitors. Fork loop 2 sequence is shaded yellow, a relevant portion of β homology region D is shaded green, and a proposed flexible region of the bridge α-helix (from simulation) is shaded red. Hydrogen bonds are indicated with red lines. Streptolydigin (STL) disrupts a hydrogen bonding network in Tt RNAP. α-amanitin, an RNAP II inhibitor, and Microcin J25 (McJ25), a bacterial RNAP inhibitor, interact at similar positions (sites of some McJ25-resistant mutations are indicated (see Table SI and Fig. 8)). B) A snapshot of Sc RNAP II (PDB 2E2H) at 2 ns. C) A snapshot of wt Tt RNAP at 7 ns. The image shows the bridge helix (blue) and its β’ R1078 residue making backbone hydrogen bonding contact with the extended fork loop region (gray) through terminal NH nitrogens to the backbone oxygens of β P440 and β R428. The terminal NH nitrogen of R428 makes hydrogen bonding contact with the backbone oxygen of β A447 and β I449 while the R428 NE interacts with the backbone oxygen of β A423.