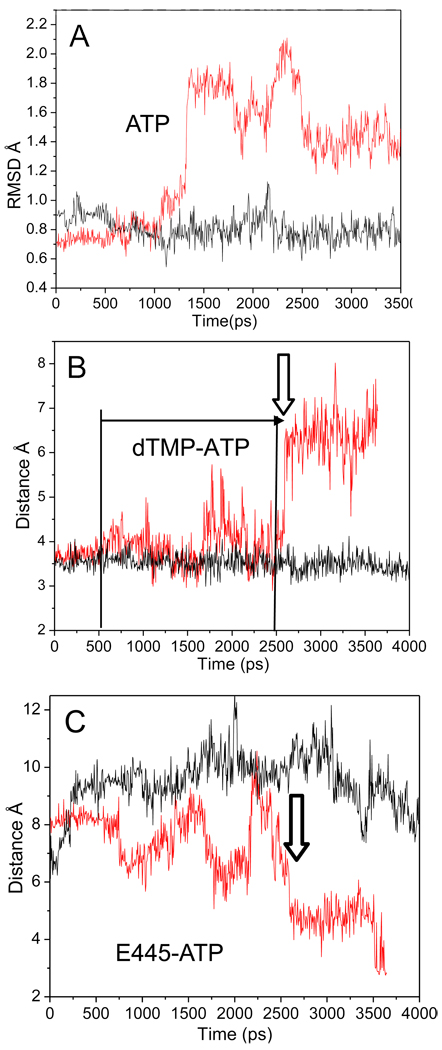
Fig. 4.
Destabilization of interactions within the R428A RNAP active site. A) RMSD of the ATP molecule of wt (black) and R428A (red). At ~1275 ps, the RMSD of the ATP substrate begins to vary in R428A from its initial structure, while wt RNAP remains stable. B) The distance between the NH2 of ATP to the carboxylate oxygen of TMP (base pair) for wt (black) and R428A (red). dTMP-ATP hydrogen bonding is observed for R428A at the time of the increase in the ATP RMSD of (~1275 ps; panel A), but base pairing becomes erratic (panel B; horizontal arrow; from ~500 ps; distance >4 Å). dTMP-ATP base pairing is lost at ~2600 ps (vertical arrow). C) The β E445 (OE1) to ATP (N6) distance of wt (black) and R428A (red). The vertical arrow indicates the time at which ATP loses hydrogen bonding with dTMP in R428A (panel B) and more closely approaches E445 (panel C).