Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of information transmission by a spiking noisy neural population. Stimuli are drawn from one of two distributions 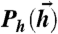 : (i) “binary” distributions, where the input to each neuron is one of the μ = 1,…,K patterns of { ± 1}, i.e.,
: (i) “binary” distributions, where the input to each neuron is one of the μ = 1,…,K patterns of { ± 1}, i.e., 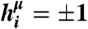 ; (ii) Gaussian distributions with given covariance matrices. These hi drive a neural response, parameterized by
; (ii) Gaussian distributions with given covariance matrices. These hi drive a neural response, parameterized by  and neural reliability β, in Eq. 2. Positive (negative) couplings between neurons Jij are schematically represented as green (red) links, with thickness indicating interaction strength. Each input drawn from
and neural reliability β, in Eq. 2. Positive (negative) couplings between neurons Jij are schematically represented as green (red) links, with thickness indicating interaction strength. Each input drawn from 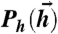 is probabilistically mapped to binary words at the output, {σi}, allowing us to define the mutual information
is probabilistically mapped to binary words at the output, {σi}, allowing us to define the mutual information 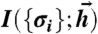 in Eq. 5 and maximize it with respect to g.
in Eq. 5 and maximize it with respect to g.

