Fig. 3.
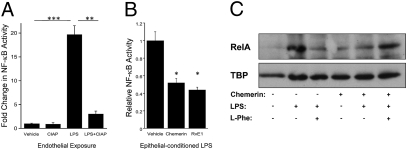
RvE-induced epithelial ALPI detoxifies LPS.(A) NF-κB activity was assessed in HMEC (endothelial) cells by luciferase-reporter assay, following exposure to 100 ng/mL LPS ± purified calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP; 1 DEA unit/mL). CIAP significantly attenuated LPS-mediated NF-κB activity (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005). (B) LPS-transfer assay involved treatment of IECs to vehicle, chemerin (1 μM) or RvE1 (100 nM) overnight, followed by exposure to fluorescently labeled LPS for 4 h. LPS was quantified by fluorometry and applied to endothelial cells transfected with a NF-κB reporter. Conditioned media from (1 μM) chemerin- and (100 nM) RvE1-treated IECs significantly detoxified LPS (*P < 0.05). (C) Western blot of HMEC-1 nuclear RelA, following 10 min incubation in conditioned medium from Caco-2 ± 1 μM chemerin overnight and ± LPS (100 ng/mL) ± L-Phe (100 nM; ALPI inhibitor) for 4 h. TBP (TATA binding protein) was used as a loading control.