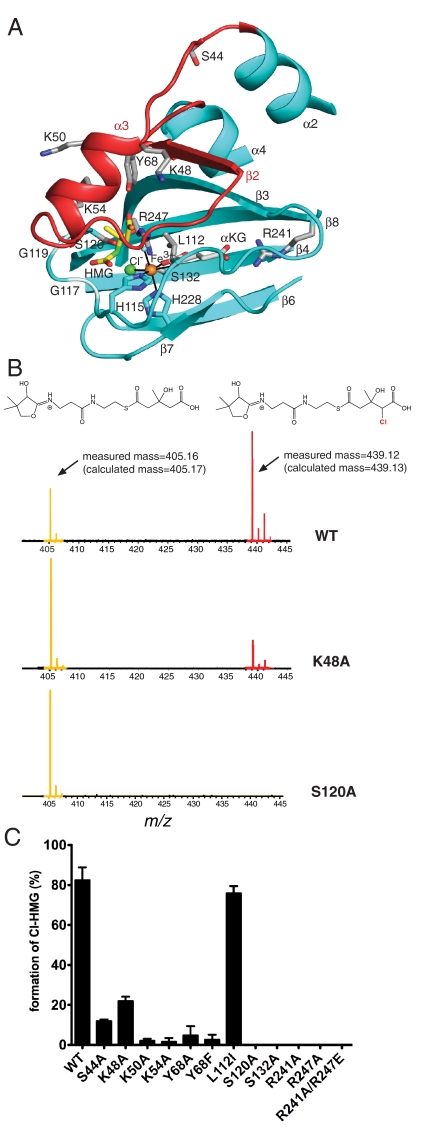
Fig. 4.
HMG model and site-directed mutagenesis of Cur Hal. (A) Model of HMG binding in the active site. Residues in contact with modeled HMG (yellow C) include Ser120 to the 3-S-hydroxyl, Tyr68 to the thioester carbonyl and the backbone at residues 117–119 to a carboxylate oxygen. The C4 atom of HMG to be chlorinated is green. Side chains of residues tested by mutagenesis are shown with gray C. (B) PPant-ejection assay of Hal activity. Substrate and product were ejected from ACP by IRMPD and detected by FTICR-MS. HMG-PPant is at m/z 405.16, Cl-HMG-PPant is at m/z 439.12. (C) Activity of wild-type and Hal mutants. Activity is represented as the percent of chlorinated product compared to total species ejected. Each reaction was performed at least in triplicate. Error bars represent the standard error of measurement.