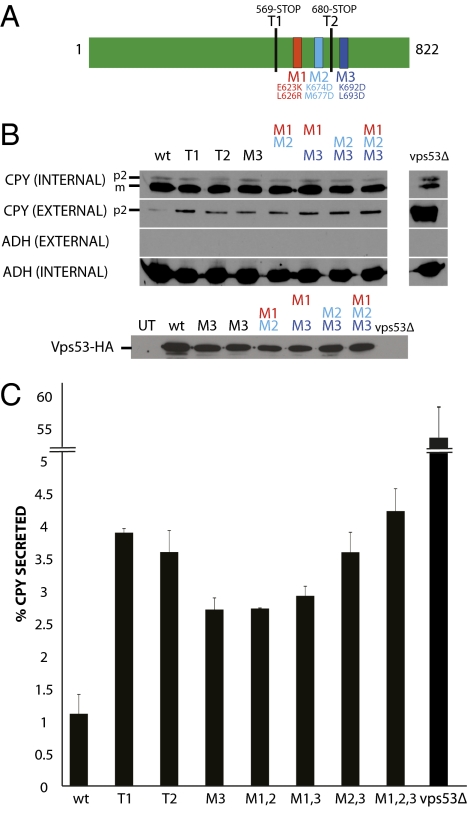
Fig. 4.
CPY secretion assays showing that the conserved surface of the Vps53 C terminus is important for membrane trafficking. (A) Schematic diagram of Vps53p and the mutations tested in the CPY secretion assay. In T1 and T2, Vps53 was truncated at residues 569 and 680, respectively. M1, E623K, L626R; M2, K674D, M677D; M3, K692D, L693D. (B) Western blots testing vps53 mutants for CPY secretion. The levels of CPY secreted into the media (external CPY) and CPY retained in the cells (internal CPY) were examined for wild-type (wt) cells and several vps53 mutants. The p2 form (Golgi-modified) and m form (mature, vacuolar) of CPY are indicated. Western blots against alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh1p) were performed to control for loading (internal ADH) and to verify that cells did not lyse upon harvesting (external ADH). Western blots against a C-terminal 3xHA-tag were used to control for levels of Vps53 constructs (except T1 and T2, which are untagged). The M3 sample was loaded twice. Levels are comparable to wild-type protein, as determined by a comparison with the ADH loading control. (C) Quantitation of the CPY secretion assays. The percentage of secreted CPY for several vps53 mutants compared with wild-type cells was quantitated from two separate trials. Error bars indicate SD (n = 2).