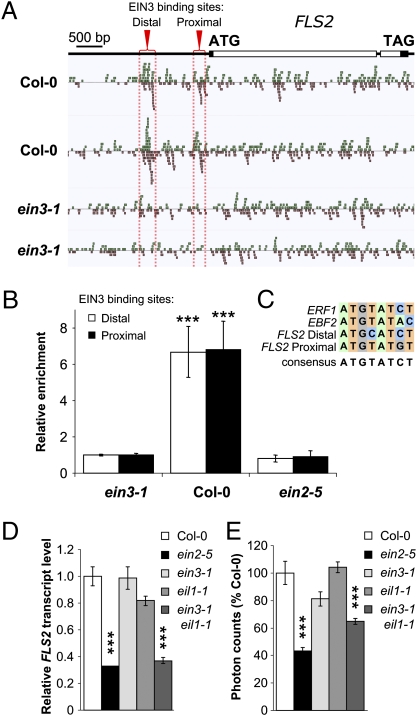
Fig. 4.
EIN3/EIL1 directly control FLS2 expression at the transcriptional level. (A) Alignment of ChIP-Seq reads across the FLS2 (At5g46330) gene and promoter region as shown with Anno-J viewer. Col-0 or ein3-1 etiolated seedlings were grown in hydrocarbon-free air for 3 d, treated with 10 ppm ethylene gas for 4 h, and then used in ChIP-Seq analysis using an anti-EIN3 polyclonal antibody. The proximal and distal regions with significant enrichment are highlighted by red brackets and dashed lines. Results from two independent experiments are presented. Reads are normalized for each sample. Gene annotation is depicted at the top; filled boxes and open boxes represent the 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions and exons of the gene, respectively. (B) Enrichment of the indicated EIN3-associated DNA fragments after ChIP-PCR. Chromatin from wild-type Col-0 and ein3-1 light-grown seedlings was immunoprecipitated with an anti-EIN3 polyclonal antibody. Enrichment of associated DNA fragments was verified by qPCR using specific primers and is presented as relative to Col-0. (C) Sequence alignment of EIN3 binding sites in ERF1, EBF2, and FLS2 promoters. EIN3 binding sites in the promoters of ERF1 (23) and EBF2 (25) are presented. Identified by ChIP-Seq, the two potential binding sites of EIN3 to the FLS2 promoter are also shown. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of FLS2 expression in Col-0, ein2-5, ein3-1, eil1-1, and ein3-1 eil1-1 seedlings. Transcript levels are normalized to the U-box housekeeping gene and are presented as relative to Col-0. Data are representative of one of two experiments. (E) Total ROS production triggered by 100 nM flg22 in Col-0, ein2-5, ein3-1, eil1-1, and ein3-1 eil1-1 mutants. Values are expressed as percentage of ROS obtained with Col-0 for 40 min and are mean ± SE (n = 20). Statistical significance by comparison with (B) ein3-1 and (C) Col-0 was assessed using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments.