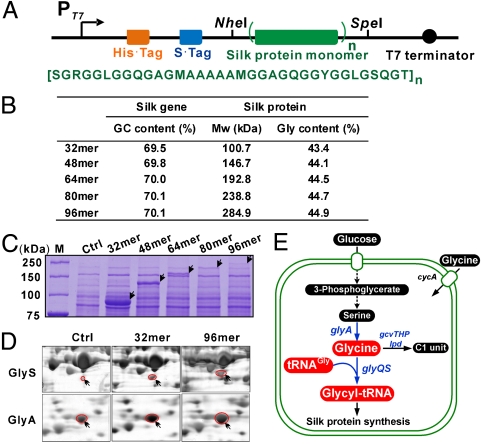
Fig. 1.
Recombinant expression of spider dragline silk proteins in Escherichia coli. (A) Recombinant spider silk protein expression constructs (Upper) (see SI Text) and amino acid sequence of the silk monomer (Lower). (B) The GC content of the silk genes and molecular weight (Mw) along with glycine content of the encoded silk proteins. (C) Coomassie-stained 10% SDS-PAGE gel analysis of lysates of E. coli BL21(DE3) cells transformed with empty vector (Ctrl) or plasmids encoding indicated silk proteins. (D) Silver-stained two-dimentional electrophoresis gel analysis of the proteomes of the cells indicated as in C. Shown are enlarged sections of β subunit (GlyS) of glycyl-tRNA synthetase and serine hydroxymethyltransferase (GlyA), the two host proteins upregulated upon silk expression. (E) The glycyl-tRNA metabolic pathways in E. coli. Glycyl-tRNA is synthesized by attaching glycine to tRNAGly by glycyl-tRNA synthetase. Intracellular glycine level is affected by the uptake of extracellular glycine, biosynthesis and degradation by the cleavage system.