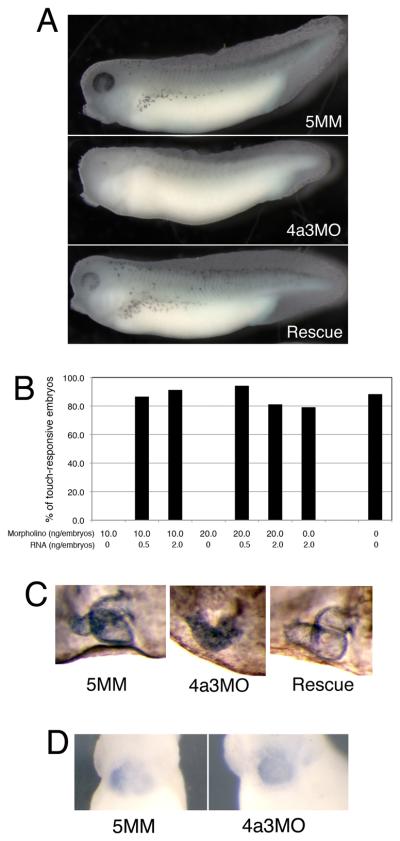
Fig. 2.
The Eif4a3 morphant phenotype. A: Loss of pigment-forming cells following Eif4a3 knockdown. 21ng of each morpholino (“4a3MO”: Eif4a3 morpholino; “5MM”: 5 base pair mismatch Eif4a3 morpholino) was injected, as listed, in this and subsequent figures. “Rescue”: Eif4a3MO+2ng eif4a3 RNA. Embryos were derived from albino eggs fertilized with sperm from wild-type males. B: Loss of touch response behavior in Eif4a3 morphants. Graph depicting percentage of touch-responsive embryos injected with listed doses of eif4a3 RNA and/or morpholino (4a3MO), as shown. C: Defects of heart formation in Eif4a3 morphants. Troponin T staining of cardiac tissue in stage 37/38 embryos injected with 4a3MO, 5MM, or 4a3MO+Eif4a3 RNA (rescue). Note lack of heart looping in 4a3MO-injected embryo. D: Whole-mount in situ hybridization with antisense probes against Xnkx-2.5 in stage 28 embryos injected with Eif4a3MO (4a3MO) or Eif4a3MM (5MM), as listed. No significant differences were seen in the expression of this marker at neurula or tailbud stages (data not shown).