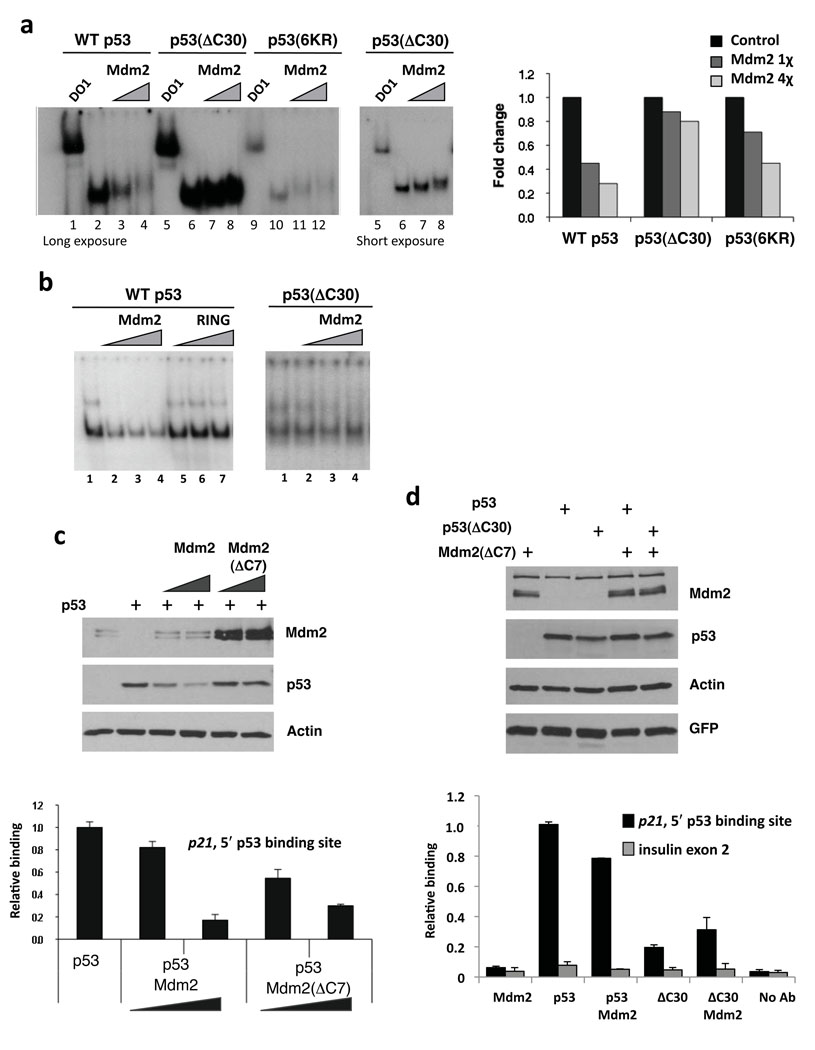
Figure 4. The p53 C-terminus is required for Mdm2 to inhibit p53 DNA binding in vitro and in cells.
(a) Deletion of the C-terminus of p53 largely alleviates the ability of Mdm2 to inhibit the p53–DNA interaction. Left panel: An EMSA performed with heparin-purified p53, p53(ΔC30) and p53(6KR) proteins. p53 bound to a 44-bp fragment spanning the 5′-p53 binding site from the p21-promoter in the presence Mdm2 (.5 or 1 µg). Right panel: graph representing data in left panel. (b) Mdm2 RING domain does not inhibit p53–DNA interaction. EMSAs were performed as in 4a. p53 (left panel) or p53(ΔC30) (right panel) (250 ng) bound DNA in the presence of Flag-tagged Mdm2 (0.5, 1 or 1.5 µg) or GST-Mdm2(410–491) (RING) (0.5, 1 or 1.5 µg). (c) Mdm2(ΔC7) impairs p53 association with p21 promoter in cells without lowering p53 protein levels. 2KO mouse cells (p53−/−;Mdm2−/−) transfected with Mdm2 or Mdm2(ΔC7) (10 and 20 µg) and p53 (4 µg). Protein expression was determined by immunoblotting with anti-Mdm2 (Smp14, 3G5 and 2A10), anti-p53 (PAb 1801 and DO1) and anti-actin antibodies (top 3 panels). Chromatin samples were amplified by Q-PCR for the 5′-p53 binding site within the p21 promoter. (d) Mdm2(ΔC7) reduces the association of p53 with the p21 promoter. 2KO cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Mdm2(ΔC7) (10 µg), p53 (4 µg), p53(ΔC30) (0.4 µg) and GFP (0.1 µg). Extracts were analyzed as in 4c and insulin exon 2 was used as a negative control.