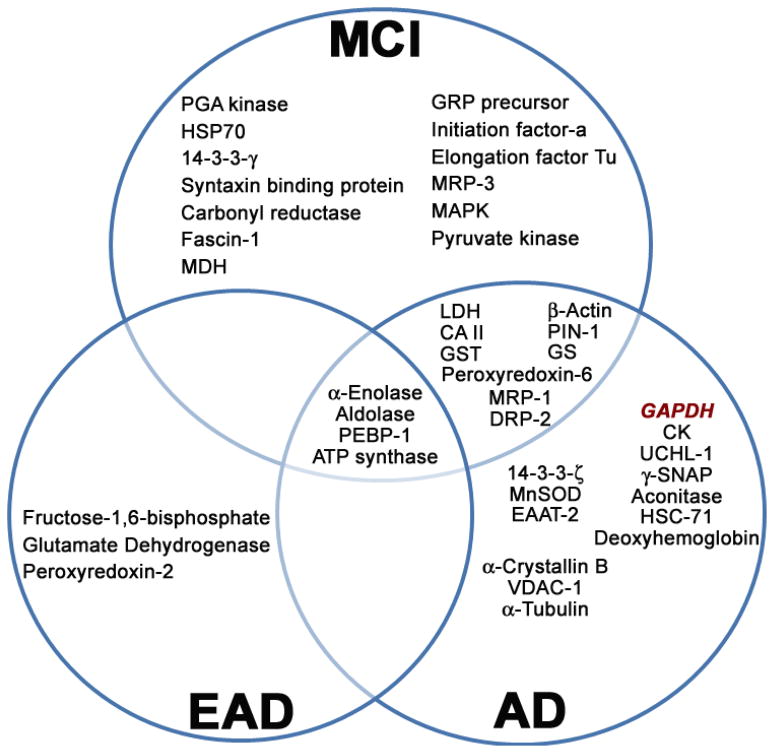
Figure 5. Proteins oxidatively modified in MCI, EAD, and AD brain identified by our laboratory [48, 51, 55, 225–231].
The inter-relationship of those proteins identified to be significantly modified by protein carbonylation, HNE- and 3-NT modification, as well as S-glutathionylation using redox proteomics on mild cognitive impairment (MCI), early AD (EAD), and AD human brain are shown. Abbreviations: PCG kinase, phosphoglycerate kinase; HSP-70, Heat-shock protein-70; MDH, Malate dehydrogenase; GRP precursor, Glucose-regulated protein precursor; MRP-1/MRP-3, Multidrug-resistant protein-1 or -3; MAPK, Mitogen-associated protein kinase; PEBP-1, phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein-1; LDH, Lactate dehydrogenase; CAII, Carbonic anhydrase II; GST, Glutathione S-transferase; DRP-2, Dihydropyrimidinase-related protein-2; PIN-1, Peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase; GS, Glutamine synthetase; MnSOD, Manganese superoxide dismutase; EAAT-2, Excitatory amino acid transporter-2; VDAC-1, Voltage dependent anion channel-1; GAPDH, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CK, Creatine kinase; UCHL-1, Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L-1; γ-SNAP, Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein-γ; HSC-71, Heat-shock cognate-71.