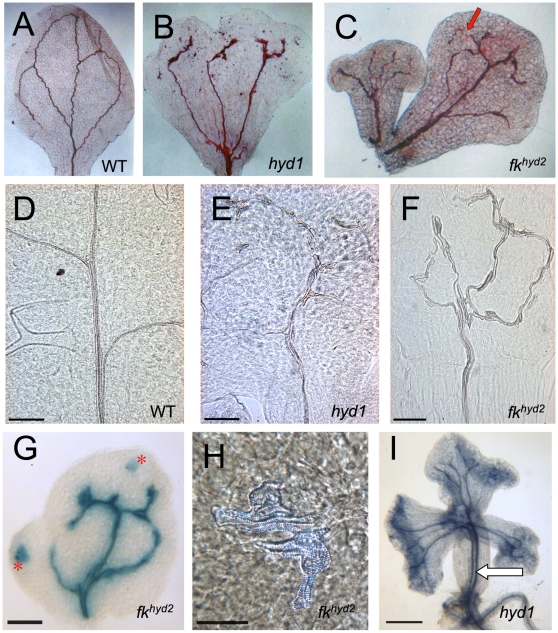
Figure 1. Vascular strand defects in hyd/fk mutant seedlings.
A: Safranine-stained wild-type cotyledon showing the tissue pattern of vascular differentiation, ×30 magnification. B: Safranine-stained hyd1 cotyledon, with dissociation of the primary vasculature into three traces, ×30 magnification. C: Safranine-stained cotyledons from a fkhyd2 seedling, with primary vascular dissociation in one of the cotyledons at the point indicated by the arrow, ×30 magnification. D–F: Cleared tissues from the central lamina of the first true leaf of 12 dpg plants of wild-type (d), hyd1 (e), fkhyd2 (f); bars = 200 µM. G: fkhyd2 cotyledon showing proPIN1::GUS expression to reveal vascular strands and ‘islands' of vascular tissue (asterisks); bar = 250 µM. H: Vascular ‘island' of disconnected xylem cells in fkhyd2 cotyledon (7 dpg) cleared with chloral hydrate; bar = 50 µm. I: Aniline blue-stained hyd1 seedling (8 dpg) showing duplicated vascular strand in the mutant (arrow) ; bar = 500 µM.