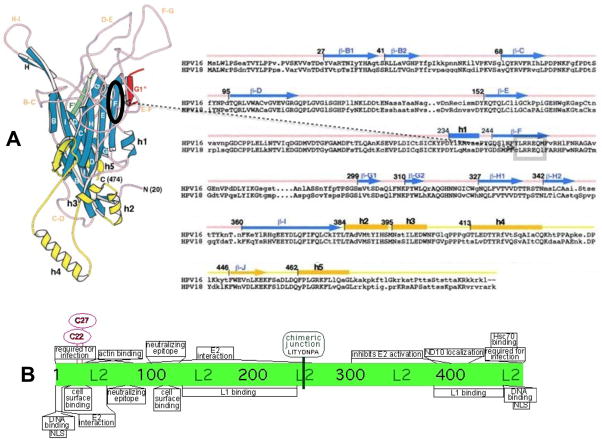
FIGURE 5.
Capsid proteins L1 and L2 chimeric junctions. Shown are the approximate positions of the cloning junctions used for the L1 and L2 HPV18 and HPV16 chimeras. (A) Shown are the three-dimensional monomeric structure of L1 (left) and the amino acid sequences of HPV16 and HPV18 L1 proteins beginning at the consensus methionine (right) as described by Chen et al. (Chen et al., 2000). On the three-dimensional structure an oval shows the region on the F ß-sheet strand containing the chimeric junction. The position of the chimeric junction can also be seen of the two-dimensional sequence inside of the box. The positions of the ß-sheets (capital letter only for the three-dimensional structure and ß-capital letter for the sequence) and the helixes (h) are shown. (B) Shown are described functional regions of papillomavirus L2 proteins (Bossis et al., 2005; Fay et al., 2004; Florin et al., 2006; Florin et al., 2002; Gornemann et al., 2002; Heino, Zhou, and Lambert, 2000; Holmgren et al., 2005; Kamper et al., 2006; Kawana et al., 1999; Laniosz, Nguyen, and Meneses, 2007; Okun et al., 2001; Roden et al., 2001; Roden et al., 1994b; Yang et al., 2003a; Yang et al., 2003b; Zhou et al., 1994). The chimeric junction is shown at its position in the center of the L2 protein.