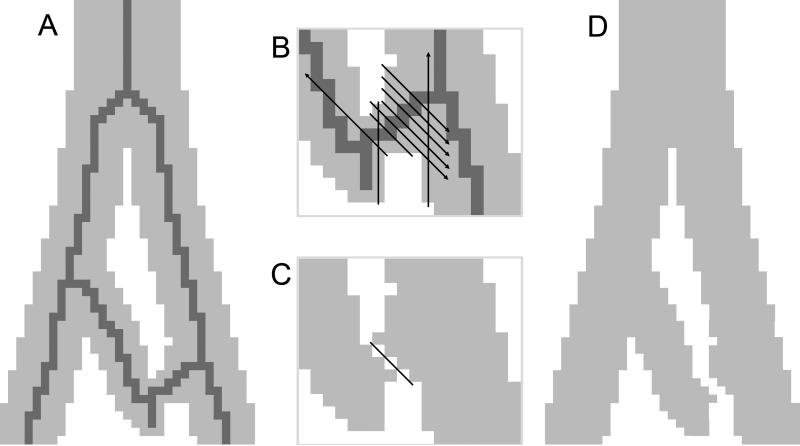
Fig. 4.
Automated loop detection and removal steps are illustrated here in two dimensions (2D) with pixels instead of voxels. A. A section of a lung airway demonstrating a loop is simplified into 2D. The skeleton generated is displayed in dark grey. B. Inset focusing on an airway branch displays black lines indicating test cuts for each pixel in the branch. Note that arrowheads on lines indicate continuance until no longer encountering airway pixels. Note also that test cuts are actually made for every branch that is part of the loop. C. The test cut which removes the least number of pixels is selected, and cutting is then performed. D. After cutting, a repair step reassigns pixels to eliminate invalid, ambiguous connections between pixels.