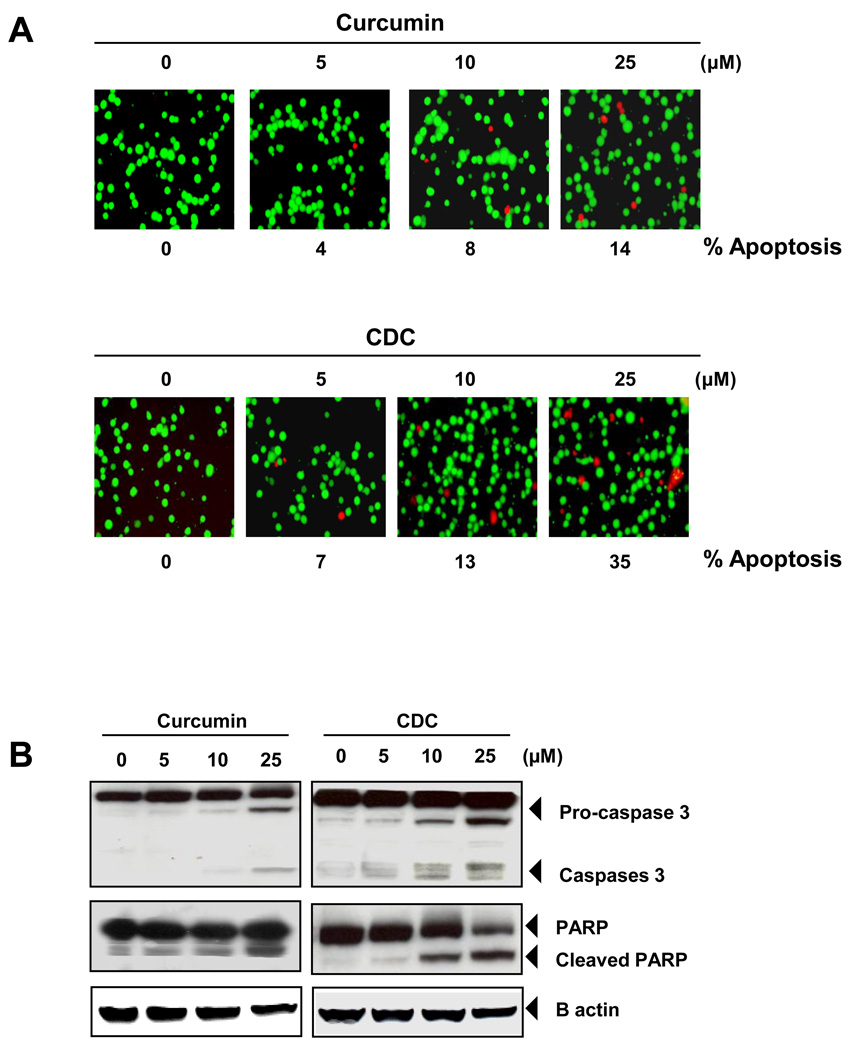
Figure 4.
CDC is more active than curcumin in inducing apoptosis. (A) KBM-5 cells (5000 cells/well) were incubated with curcumin or CDC at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. The cells were harvested and stained with Live/Dead assay reagent as per the manufacturer’s protocol as described in methods. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (B) CDC showed more apoptosis than curcumin. KBM-5 cells were treated with (5–25 µM) CD, curcumin or CDC for 24hr. Cleavage of caspase-3, and poly (ADP ribose) polymerase were determined by western blotting in whole-cell extracts of CD, Curcumin, and CDC treated cells. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) CDC showed more cell death than curcumin. KBM cells (2 × 106/mL) were synchronized by incubation overnight in the absence of serum and then treated with (5–25 µM) CD, curcumin and CDC for 24hr, after which the cells were washed, fixed, stained with propidiumiodine and analyzed for DNA content by flow cytometry. (D) KBM-5 cells were treated with (5–25 µM) CD, curcumin and CDC for 24hr. Cell death was determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting using annexin V/propidium iodide staining