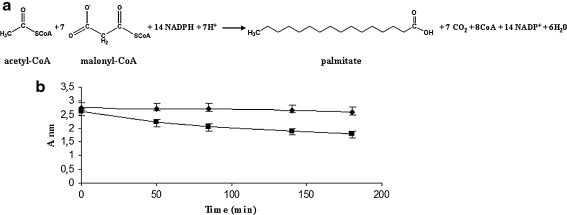
Fig. 2.
FAS-B catalysis and assay. a The Stoichiometry of the synthesis of palmitate controlled by the FAS-B enzyme from Brevibacterium ammoniagenes. The acetyl-CoA primes the reaction, while the elongation steps are sustained by malonyl-CoA. The free energy needed for the FAS functions is provided by the decarboxilation of the malonyl-CoA. Reducing power is provided by the oxidation of 14 molecules of NADPH for each molecule of palmitate. b FAS-B enzyme assay measuring the NADPH disappearance (oxidation) spectrophotometrically. The decline of absorbance of NADPH, when the FAS-B catalysis is active, (square) in comparison with the absorbance measured when malonyl-CoA was omitted, (circle). Each value reported in the graph equal the delta between the absorbance at 340 and 600 nm wavelength. The error bars reported in the graph represent the range of values of experiments performed in triplicate